A new screening tool for early recognition of ATTRv polyneuropathy in clinical practice: AmyloScan®
- PMID: 40903555
- PMCID: PMC12408649
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-025-13338-z
A new screening tool for early recognition of ATTRv polyneuropathy in clinical practice: AmyloScan®
Abstract
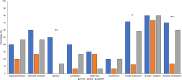
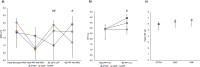
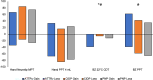
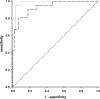
Hereditary transthyretin (ATTRv) amyloidosis is a progressive multisystem disorder, mainly characterized by cardiac dysfunction and polyneuropathy. Due to its rarity and heterogeneous presentation, diagnosis is often delayed, which has a direct impact on the initiation of treatment and, therefore, span and quality of life. To facilitate early disease recognition, we aimed to develop and validate a new screening tool for early identification of ATTRv amyloidosis with polyneuropathy (AmyloScan®). Potential disease characteristics were identified via literature screening, interviews and detailed examination of ATTRv amyloidosis patients (n = 10) and controls (CIDP: chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, n = 15; diabetic polyneuropathy, n = 15) using validated questionnaires, and autonomic and sensory testing. The preliminary AmyloScan® was developed and validated in patients with polyneuropathy caused by ATTRv amyloidosis (n = 21), CIDP (n = 19), or others (n = 43). By sensitivity and discriminant analyses, we determined the most characteristic item combinations for ATTRv amyloidosis. Cut-off values were defined by Receiver Operator Curves. The final AmyloScan® includes 12 questions and two sensory bedside tests. All items require simple yes/no answers, resulting in a total score of 0-14 points and two cut-off values: A value of ≥ 4 indicates an increased chance (sensitivity: 95.2%, specificity: 72.6%); a value of ≥ 6 indicates a high chance of ATTRv polyneuropathy (sensitivity: 81.0%, specificity: 93.5%). The AmyloScan® is a simple time- and cost-efficient screening tool with a high discriminative value. Regular use in clinical practice might enable an earlier diagnosis with impact on treatment considerations and quality of life.
Keywords: Bedside sensory test; CIDP; Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis; Red flags; TTR silencers; TTR stabilizers.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: Juliane Sachau received travel support from Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc. and Pfizer, consultant fees from Pfizer Pharma GmbH and AstraZeneca GmbH and speaker fees from Grünenthal GmbH, AstraZeneca and Alnylam Germany GmbH. Maike F. Dohrn received financial reimbursement for consulting and advisory board activities and travel support to attend scientific meetings by Akcea Therapeutics Inc., Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc., Astra Zeneca PLC, Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, and SOBI GmbH. She further received research funding by Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (ASPIRE 2018). She is a consultant for Applied Therapeutics Inc. Jan Vollert has holds an investigator-initiated grant funded by Viatris. Katrin Hahn received financial reimbursement for consulting, advisory board activities, speaker fees, and/or contributions to congresses and travel support to attend scientific meetings by Akcea Therapeutics Inc., Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc., Amicus, AstraZeneca, GSK, Hormosan, Takeda Pharmaceutical Inc., Pfizer Pharmaceuticals Inc., and Swedish Orphan Biovitrum Inc. and ViiV Healthcare GmbH. KH further received research funding by the foundation Charité (BIH clinical fellow), Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc., and Pfizer Pharmaceuticals. Timon Hansen participated in advisory boards and/or received speaker fees from Alexion, Alnylam, Amgen, BMS, GSK, Janssen, Oncopeptides, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Stefan Gingele reports research support from Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, CSL Behring, Else Kröner Fresenius Foundation, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, and Hannover Biomedical Research School (HBRS) and consulting and/or speaker honoraria from Alexion, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, GSK, Pfizer, Merck, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals all outside the submitted work. Elena Enax-Krumova holds an endowed professorship funded by the German Social Accident Insurance (DGUV) since 2019, has received a grant from the Georg Agricola Ruhr foundation and from the Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Technologie (grant nr. 50WK2273B) as well as personal fees from Novartis GmbH, Casquar GmbH, OmegaPharma GmbH and painCert GmbH. Ralf Baron reports grant/research support by EU Projects: “Europain “ (115007). DOLORisk (633491). IMI Paincare (777500), German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF): Verbundprojekt: Frühdetektion von Schmerzchronifizierung (NoChro) (13GW0338C), German Research Network on Neuropathic Pain (01EM0903), Pfizer Pharma GmbH, Sanofi Genzyme GmbH, Grünenthal GmbH, Mundipharma Research GmbH und Co. KG., Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc., Zambon GmbH, Bayer AG, and Sanofi Aventis GmbH; speaker fees from Pfizer Pharma GmbH, Sanofi Genzyme GmbH, Grünenthal GmbH, Mundipharma, Lilly GmbH, Desitin Arzneimittel GmbH, Teva GmbH, Bayer AG, MSD GmbH, Seqirus Australia Pty. Ltd, Novartis Pharma GmbH, TAD Pharma GmbH, Grünenthal SA Portugal, Grünenthal Pharma AG Schweiz, Grünenthal B.V. Niederlande, Evapharma, Takeda Pharmaceuticals International AG Schweiz, Ology Medical Education Netherlands, Ever Pharma GmbH, Amicus Therapeutics GmbH, Novo Nordisk Pharma GmbH, Chiesi GmbH, Stada Mena DWC LLC Dubai, Hexal AG, and Viatris; and consultant fees from Pfizer Pharma GmbH, Sanofi Genzyme GmbH, Grünenthal GmbH, Lilly, Novartis Pharma GmbH, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Biogenidec, AstraZeneca GmbH, Daiichi Sankyo, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals S.A., Seqirus Australia Pty. Ltd, Teva Pharmaceuticals Europe Niederlande, Teva GmbH, Genentech, Mundipharma International Ltd. UK, Galapagos NV, Kyowa Kirin GmbH, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc., Biotest AG, Celgene GmbH, Desitin Arzneimittel GmbH, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. USA, Theranexus DSV CEA Frankreich, Abbott Products Operations AG Schweiz, Bayer AG, Grünenthal Pharma AG Schweiz, Akcea Therapeutics Germany GmbH, Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation, AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG, Air Liquide Sante International Frankreich, Alnylam Germany GmbH, Lateral Pharma Pty Ltd, Hexal AG, Angelini, Janssen, SIMR Biotech Pty Ltd Australien, Confo Therapeutics N. V. Belgium, Merz Pharmaceuticals GmbH, Neumentum Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. Switzerland, AlgoTherapeutix SAS France, Nanobiotix SA France, and AmacaThera Inc. Canada. Lena Rhode, Stefanie Rehm, Manon Sendel, Thomas Skripuletz, and Klarissa Stürner do not report competing interests. Ethical approval: This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the local Ethics Committee of the Medical Faculty, Christian-Albrechts-University Kiel (Date October 22, 2019/No. 547/19). Consent to participate: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Figures

References
-
- Adams D, Koike H, Slama M, Coelho T (2019) Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis: a model of medical progress for a fatal disease. Nat Rev Neurol 15:387–404. 10.1038/s41582-019-0210-4 - PubMed
-
- Visser NA, Notermans NC, Linssen RSN et al (2015) Incidence of polyneuropathy in Utrecht, the Netherlands. Neurology 84:259–264. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001160 - PubMed
-
- Koike H, Tanaka F, Hashimoto R et al (2012) Natural history of transthyretin Val30Met familial amyloid polyneuropathy: analysis of late-onset cases from non-endemic areas. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:152–158. 10.1136/jnnp-2011-301299 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

