Combined Metformin and Baricitinib Therapy Attenuates Inflammation in STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats via AMPK/JAK-STAT Pathway Crosstalk
- PMID: 40903907
- PMCID: PMC12408610
- DOI: 10.1002/edm2.70101
Combined Metformin and Baricitinib Therapy Attenuates Inflammation in STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats via AMPK/JAK-STAT Pathway Crosstalk
Abstract
Background: Chronic inflammation is a critical factor contributing to diabetes complications. Baricitinib inhibits JAK-STAT signalling, which can contribute to an anti-inflammatory effect. Similarly, metformin demonstrates anti-inflammatory properties by activating the AMPK-SIRT pathway and suppressing the NF-ᴋB signalling pathway. Here, we explored the effects of the coadministration of metformin and baricitinib in diabetic rats.
Methods: Streptozotocin (40 mg/kg body weight) was administered to rats to develop diabetes after 2 weeks of 10% fructose solution consumption. The rats were treated with baricitinib (0.5, 2.5 and 5 mg/kg) and 150 mg/kg metformin for 1 month. A dose of 0.5 mg/kg baricitinib was chosen for combination therapy with metformin.
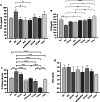
Key findings: Baricitinib induced significant weight loss at all three doses (p ≤ 0.05) and significantly increased lipid profile parameters in comparison to the diabetic control group (p ≤ 0.05). Pancreatic NF-ᴋB levels and HOMA-IR were meaningfully reduced in all treatment groups (p ≤ 0.01). Metformin and combination therapy significantly reduced serum TNF-α levels (p ≤ 0.05). Furthermore, baricitinib at different doses and combination therapy significantly elevated serum IL-10 levels (p ≤ 0.05). Additionally, combination therapy significantly upregulated the liver expression of NF-ᴋB, SOCS1, SOCS3, AMPK and SIRT-1 (p ≤ 0.01).
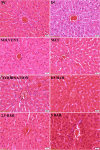
Conclusion: Our results suggest that the coadministration of metformin with baricitinib reduces insulin resistance, improves histopathological alterations in the liver and pancreatic islet cells and counteracts the adverse effects of baricitinib on the lipid profile in diabetic rats. These findings hold particular significance for patients undergoing baricitinib treatment.
Keywords: AMPK; JAK–STAT; NF‐kB; SIRT1; baricitinib; metformin.
© 2025 The Author(s). Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
A potential conflicts of interest has not been identified by the authors in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Roden M. and Shulman G. I., “The Integrative Biology of Type 2 Diabetes,” Nature 576, no. 7785 (2019): 51–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

