Accelerated Navigator for Rapid ∆B0 Field Mapping for Real-Time Shimming and Motion Correction of Human Brain MRI
- PMID: 40905334
- PMCID: PMC12409692
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.70126
Accelerated Navigator for Rapid ∆B0 Field Mapping for Real-Time Shimming and Motion Correction of Human Brain MRI
Abstract
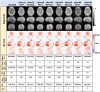
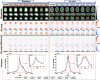
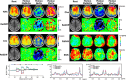
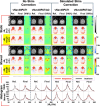
∆B0 shim optimization performed at the beginning of an MR scan is unable to correct for ∆B0 field inhomogeneities caused by patient motion or hardware instability during scans. Navigator-based methods have been demonstrated previously to be effective for motion and shim correction. The purpose of this work was to accelerate volumetric navigators to allow fast acquisition of the parent navigated sequence with short real-time feedback time and high spatial resolution of the ∆B0 field mapping. A GRAPPA-accelerated 3D dual-echo EPI vNav was implemented on a 3 T Prisma MRI scanner. Testing was performed on an anthropomorphic head phantom and 11 human participants. vNav-derived ∆B0 field maps with various spatial resolutions were compared to Cartesian-encoded gold-standard 3D gradient-echo ∆B0 field mapping. ∆B0 shimming was evaluated for the scanner's spherical harmonics shims and a custom-made AC/DC RF-receive/∆B0-shim array. The performance of dual-echo and single-echo accelerated navigators was compared for tracking and updating ∆B0 field maps during motion. Real-time motion and shim corrections for 2D MRI and 3D MRSI sequences were assessed in vivo with controlled head movement. Up to 8-fold acceleration of volumetric navigators (vNavs) significantly reduced geometric distortions and signal dropouts near air-tissue interfaces and metal implants. Acceleration allowed a flexible tradeoff between spatial resolution (2.5-7.5 mm) and acquisition time (242-1302 ms). Notably, accelerated high-resolution (5 mm) vNav was faster (378 ms) than unaccelerated low-resolution (7.5 mm) vNav (700 ms) and showed better agreement with 3D-GRE ∆B0 field mapping with 5.5 Hz RMSE, 1 Hz bias, and [-10%, +10%] confidence interval. Accelerated vNavs improved 3D MRSI and 2D MRI in real-time motion and shim correction applications. Advanced shimming with spherical harmonic and shim array showed superior ΔB0 correction, especially with joint shim optimization. GRAPPA-accelerated vNavs provide fast, robust, and high-quality ∆B0 field mapping and shimming over the whole-brain. The accelerated vNavs enable rapid correction of ∆B0 field inhomogeneities and faster acquisition of the navigated parent sequence. This methodology can be used for real-time motion and shim correction to enhance data quality in various MRI applications.
Keywords: GRAPPA acceleration; magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI); motion correction; multi‐coil shim array; real‐time shimming; spherical harmonic shims; volumetric navigators (vNavs); ΔB₀ field mapping.
© 2025 The Author(s). NMR in Biomedicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures






References
-
- Wezel J., Boer V. O., van der Velden T. A., et al., “A Comparison of Navigators, Snap‐Shot Field Monitoring, and Probe‐Based Field Model Training for Correcting B 0‐Induced Artifacts in ‐Weighted Images at 7 T,” Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 78, no. 4 (2017): 1373–1382, 10.1002/mrm.26524. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

