Diagnosed Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B and Delta Virus in Italy in 2024: An Estimation From a National Real-World Database
- PMID: 40905613
- PMCID: PMC12410042
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.70336
Diagnosed Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B and Delta Virus in Italy in 2024: An Estimation From a National Real-World Database
Abstract
Background and aims: Hepatitis B (HBV) and Hepatitis Delta virus (HDV) infection have undergone significant changes in Italy over the past few decades, but reliable and updated prevalence of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and Delta (CHD) data are lacking. The aim of the study was to describe the epidemiology of CHB and CHD in Italy in 2024, based on real-world data.
Methods: The number of patients with a healthcare expenditure exemption for CHB (016.070.32) and CHD (016.070.33) was obtained from 21 Regional Health Authorities. To understand how many CHB or CHD patients did not have these specific exemptions, a survey was conducted in 30 Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Infectious Diseases Units across the country.
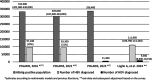
Results: Health Authorities data reported 67 514 and 5216 subjects with an exemption for CHB and for CHD, respectively. However, among 6775 CHB and 504 CHD patients, only 60.3% and 55.7% of them had the specific exemption, respectively. Based on these results, we estimated 111 960 (95% CI: 109 780-114 240) CHB and 9360 (95% CI: 8690-10 150) CHD patients, with a prevalence of 0.22% and 0.019% of the adult overall population. Moreover, anti-HDV prevalence was 7.7% from this cohort.
Conclusion: Our study provides a plausible estimate of the current number of adult patients diagnosed with CHB and CHD in Italy and may be considered the basis for decision-making health policies.
Keywords: HBV; HDV; Italy; epidemiology; prevalence.
© 2025 The Author(s). Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Alessandro Loglio: Speaker bureau and received grants from Gilead Sciences and Roche. Laura Schiadà: travel grants from Astra Zeneca, Roche, MSD. Fee for lectures and expertise from Astra Zeneca. Ivan Gentile: consultant for MSD, AbbVie, Gilead, Pfizer, GSK, Astrazeneca, Basilea, SOBI, Nordic/InfectoPharm, Angelini, Moderna, Shionogi, Advanz Pharma, Abbott and Mundipharma Pharmaceuticals. Maurizia Rossana Brunetto: Advisory for Gilead, Roche; Speakers Bureau: AbbVie, Gilead, EISAI‐MSd, AstraZeneca. Loredana Sarmati: travel grants from Gilead, Merck, Pfizer, fee for lectures and expertise from Merck, Gilead, Abbvie, Angelini, Astra Zeneca, GSK. Francesca Romana Ponziani: received speaker fees, advisory board fees and travel grants from Bayer, MSD, Roche, Eisai, Ipsen, Astra‐Zeneca, Gilead, Abbvie. Morisco Filomena: Advisory board for Gilead, Ipsen, Astra Zeneca, Mirum, Roche Diagnostic, Aboca, Alfa‐Sigma. Pierluigi Toniutto: Advisory Gilead, Roche, Astra Zeneca; Speakers Bureau: AbbVie, Gilead, EISAI‐MSd, AstraZeneca. Edoardo Giovanni Giannini: Advisory Board, AstraZeneca, Gilead, Ipsen, Roche; Teaching & Speaking: AstraZeneca, Gilead, Ipsen, Roche. Dante Romagnoli: Advisory Board for AbbVie and Gilead Sciences. Giuseppe Cabibbo: Advisory board/Speaker for Bayer, Eisai, Ipsen, and AstraZeneca, MSD, Roche, Gilead. Pietro Lampertico: Advisory Board/Speaker Bureau for: Roche Pharma/Diagnostics, Gilead Sciences, GSK, Abbvie, Janssen, MYR, Eiger, Antios, Aligos, VIR, Grifols, Altona, Roboscreen. Pietro Invernizzi: travel grants from Gilead, Ipsen, fee for lectures and expertise from Calliditas, Gilead, Zydus, Ipsen, GSK. Antonio Ciaccio: Speaker bureau for Gilead, Abbvie, AlfaSigma. Gerardo Nardone: Speaker for Allergosan, Alfasigma. Alessandro Federico: Advisory Board for Gilead, Alfasigma. Vincenzo Messina: Advisory Board for Abbvie, Gilead, MSD, Roche. Ernesto Claar: research grant from Gilead Sciences. Valerio Rosato: research grants from Gilead, advisory board from Gilead and MSD. Gianpiero D'Offizzi: Advisory Board for AbbVie, Gilead, Viatris, GSK. Paolo Caraceni: Advisory Board for Abbvie, lecturer for Gilead. Mauro Viganò: Advisory Board/Speaker Bureau for: Gilead Sciences, Ipsen. Others declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- “Global Hepatitis Report 2024: Action for Access in Low‐ and Middle‐Income Countries,” accessed February 28, 2025, https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240091672.
-
- Sagnelli E., Stroffolini T., Sagnelli C., et al., “Influence of Universal HBV Vaccination on Chronic HBV Infection in Italy: Results of a Cross‐Sectional Multicenter Study,” Journal of Medical Virology 89 (2017): 2138–2143. - PubMed
-
- Zanetti A. R., Romanò L., Zappá A., and Velati C., “Changing Patterns of Hepatitis B Infection in Italy and NAT Testing for Improving the Safety of Blood Supply,” Journal of Clinical Virology 36 (2006): S51–S55. - PubMed
-
- Mele A., Tosti M. E., Mariano A., et al., “Acute Hepatitis B 14 Years After the Implementation of Universal Vaccination in Italy: Areas of Improvement and Emerging Challenges,” Clinical Infectious Diseases 46 (2008): 868–875. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous