Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis of Jinggang honey pomelo yellow spot disease to reveal the disease resistance mechanism
- PMID: 40906757
- PMCID: PMC12410739
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0330626
Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis of Jinggang honey pomelo yellow spot disease to reveal the disease resistance mechanism
Abstract
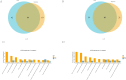
Jinggangshan honey pomelo is a specialty fruit grown in Jiangxi Province, China. Pomelo yellow spot disease, also known as greasy spot disease, is a fungal pathology primarily affecting pomelo (Citrus maxima) leaves and fruits. The causative agent is the ascomycete fungus Phyllosticta citricarpa, taxonomically classified within the phylum Ascomycota.This study performed integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis to identify key differentially accumulated metabolites (DAMs) and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the control (CK) and diseased groups (HB) of the Jinlan pomelo (af) and Jinsha pomelo (js) varieties. We identified 1,681 DAMs in the af variety and 1,233 DAMs in the jsCK_vs_jsHB variety. Flavonoid compounds were the most upregulated class of DAMs in both the af and js diseased varieties. Transcriptome analysis identified 1,714 common DEGs between the af and js diseased varieties. KEGG pathway enrichment analysis demonstrated that these common DEGs were significantly enriched in pathways such as plant hormone signal transduction, plant-pathogen interaction, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, MAPK signaling pathway in plants, and flavonoid biosynthesis. The integrated metabolome and transcriptome analysis showed that the metabolic pathways associated with the common DEGs and DAMs in both the af and js varieties were significantly enriched in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway. Our data showed that differential expression of key enzymes in the flavonoid biosynthesis and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathways led to the accumulation of flavonoid metabolites, which play a crucial role in the plant defense mechanisms against external stresses, including pathogen infection. The results suggest that the flavonoid compounds play a key role in the disease resistance mechanism of Jinggangshan honey pomelo against yellow spot disease.
Copyright: © 2025 Sun et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Xin-sheng X, Zi-long S, Yong-yan X, Zhi-hui Y. Comparison of components, antioxidant and bacteriostatic ability of different varieties of pomelo peel essential oil. Nat Prod Res Dev. 2024;36:218.
-
- Lu XY, Chen Z, Tang F, Fu SL, Ren J. Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals mechanism of anthocyanin changes in red maple (Acer rubrum) leaves. CABI Databases. 2020;:38–54.
-
- Fu R, Chen C, Wang J, Zhao L, Chen X, Lu D. Combined transcriptome and metabolome analyses reveals the pathogenic factors of Ustilaginoidea virens. Chin J Rice Sci. 2024;38:375.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

