Epigenetic modulation of BARD1 to enhance anti-VEGF therapy
- PMID: 40907495
- PMCID: PMC12490209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102329
Epigenetic modulation of BARD1 to enhance anti-VEGF therapy
Abstract
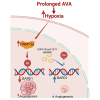
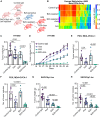
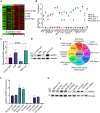
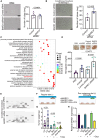
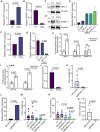
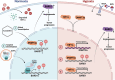
Despite the clinical use of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibodies (AVAs) in cancer therapy, resistance frequently develops, leading to disease progression. To address this, we identify a previously unknown role for breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1)-associated RING domain 1 (BARD1) in modulating AVA sensitivity. Epigenetic modulation-via global and targeted DNA methylation-reveals BARD1 as a key regulator of angiogenesis. Sequential treatment with azacytidine overcomes AVA resistance in vivo. To enable precise epigenetic reactivation, we develop a liposomal CRISPR-deactivated Cas9 (dCas9)-TET1 system guided by BARD1-targeting single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs). This platform achieves CpG-specific demethylation of the BARD1 promoter, restores expression, and enhances AVA response. Additionally, BARD1 restoration, through either dCas9-TET1 or small interfering RNA (siRNA), significantly reduces tumor growth in combination with AVA in ovarian cancer models. These findings uncover a previously unrecognized function of BARD1 in tumor angiogenesis and demonstrate the potential of gene-specific epigenetic targeting to overcome AVA resistance.
Keywords: AVA resistance; BARD1; anti-VEGF antibody therapy; bevacizumab; epigenetic editing; epigenetic therapy; ovarian cancer.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.K.S.: consulting (Onxeo, ImmunoGen, and Kaida), DSMB (Advenchen and Mural Oncology), and research grant (Pfizer). C.I. contributed to the analysis during her time at MDACC; she is currently working at Caris Life Sciences as a data scientist. We declare that we have submitted a patent application related to dCas9-TET1-sgRNA.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

