The Impact of Environmental Degradation on Agricultural Crop Productivity: The Case of Pakistan With Simulated ARDL Approach
- PMID: 40909260
- PMCID: PMC12406087
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.70876
The Impact of Environmental Degradation on Agricultural Crop Productivity: The Case of Pakistan With Simulated ARDL Approach
Abstract
Environmental degradation is a cross-cutting issue that significantly hampers the productivity of the agriculture sector in Pakistan. The objective of this study is to investigate the impact of environmental degradation on agricultural productivity in Pakistan from 1973 to 2021. The study employed the Novel Dynamic Simulated Autoregressive Distributed Lag (NDS-ARDL) estimator as a data analysis technique to gauge the impact of environmental degradation (measured by CO2) and other variables, including agricultural credit, quality seeds, fertilizers, and the availability of irrigation water, on agricultural productivity. The major finding of this study shows that the impact of CO2 on crop productivity is negative but insignificant in both the short and long run. However, water availability, quality of seeds used, credit used for agriculture, and fertilizer use have a positive and significant impact in both the long and short run. Productivity improves with increased credit disbursement, quality seeds, and irrigation water. Based on these findings, policymakers should prioritize ensuring the stable and reliable availability of irrigation water supplies, promoting certified high-quality seeds, expanding access to agricultural credits, discouraging ineffective land expansion, and planning for better land use to avoid the overuse of marginal lands, thereby enhancing crop productivity in Pakistan.
Keywords: CO2 emissions; NDS‐ARDL; Pakistan; crop productivity.
© 2025 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
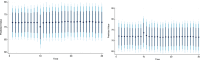
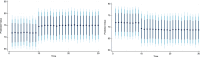
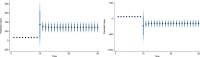
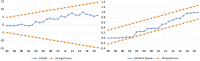
Figures




References
-
- Abbas, S. 2022. “Climate Change and Major Crop Production: Evidence From Pakistan.” Environmental Science and Pollution Research 29, no. 4: 5406–5414. - PubMed
-
- Abbas, S. , Kousar S., Shirazi S. A., Yaseen M., and Latif Y.. 2021. “Illuminating Empirical Evidence of Climate Change: Impacts on Rice Production in the Punjab Regions, Pakistan.” Agricultural Research 11, no. 1: 32–47. 10.1007/s40003-021-00548-w. - DOI
-
- Abbas, S. , Kousar S., Shirazi S. A., Yaseen M., and Latif Y.. 2022. “Illuminating Empirical Evidence of Climate Change: Impacts on Rice Production in the Punjab Regions, Pakistan.” Agricultural Research 11: 1–16.
-
- Amaefule, C. , Shoaga A., Ebelebe L., and Adeola A.. 2023. “Carbon Emissions, Climate Change, and Nigeria's Agricultural Productivity.” European Journal of Sustainable Development Research 7, no. 1: em0206.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

