This is a preprint.
Plasma membrane accessible cholesterol is regulated by ACC1 and lipid droplets
- PMID: 40909529
- PMCID: PMC12407704
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.08.21.671640
Plasma membrane accessible cholesterol is regulated by ACC1 and lipid droplets
Abstract
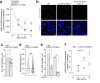
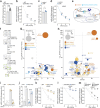
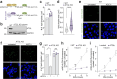
Proper maintenance of plasma membrane (PM) cholesterol is essential for diverse processes ranging from animal development to pathogen evasion. Despite decades of study, the mechanisms governing cellular cholesterol regulation are incomplete. Using genome-wide screens we find that ACC1, the rate-limiting enzyme in fatty acid biosynthesis, regulates PM cholesterol transport. ACC1 loss causes a ~10-fold increase in PM accessible cholesterol in cells and mice. Mechanistically, we find that ACC1 regulates lipid droplet (LD) catabolism, and LDs are intimately tied to PM accessible cholesterol levels since reductions or elevations in their numbers block or promote cholesterol trafficking, respectively. Furthermore, LDs are required for cholesterol trafficking induced by 25-hydroxycholesterol, a modulator of inflammation and an interferon-stimulated second messenger that protects cells from pathogen invasion. This work identifies an unrecognized role for ACC1 and LDs in cholesterol regulation, which has implications for diseases where LD numbers are altered, from metabolic syndromes to neurodegeneration.
Keywords: 25-hydroxycholesterol; ACAT1 and ACAT2; ACC1; AMPK; ATGL; Cholesterol; SREBP2; accessible cholesterol; cholesterol esters; lipid droplet; membrane trafficking; plasma membrane; triacylglycerol.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: JAO is a member of the scientific advisory board for Vicinitas Therapeutics.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Adenovirus Modulates Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling by Reprogramming ORP1L-VAP Protein Contacts for Cholesterol Transport from Endosomes to the Endoplasmic Reticulum.J Virol. 2017 Feb 28;91(6):e01904-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01904-16. Print 2017 Mar 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28077646 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Lipid droplet targeting of the lipase coactivator ABHD5 and the fatty liver disease-causing variant PNPLA3 I148M is required to promote liver steatosis.J Biol Chem. 2025 Feb;301(2):108186. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108186. Epub 2025 Jan 13. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39814233 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Droplets: Formation, Degradation, and Their Role in Cellular Responses to Flavivirus Infections.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 24;12(4):647. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040647. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kumar G. A., Jafurulla M. & Chattopadhyay A. The membrane as the gatekeeper of infection: Cholesterol in host-pathogen interaction. Chem. Phys. Lipids 199, 179–185 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
