This is a preprint.
RNA binding by ADARs prevents RNA interference from attacking self-produced dsRNA
- PMID: 40909659
- PMCID: PMC12407824
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.08.28.672520
RNA binding by ADARs prevents RNA interference from attacking self-produced dsRNA
Abstract
The ability of an organism to identify self and foreign RNA is central to eliciting an immune response in times of need while avoiding autoimmunity. As viral pathogens typically employ double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), host identification, modulation, and response to dsRNA is key. However, dsRNA is also abundant in host transcriptomes, raising the question of how these molecules can be differentiated. Two host pathways that regulate dsRNA are A-to-I RNA editing by adenosine deaminases (ADARs), and RNA interference (RNAi). Both mechanisms are important for normal organism development and function by regulating gene expression. Herein, we studied the structure and amount of siRNAs at editing sites and the ability of ADARs to prevent exogenous RNAi using the model organism, Caenorhabditis elegans. We found that the number of siRNAs targeting edited genes is significantly upregulated in ADAR mutant animals. We also found that despite an almost complete depletion of primary siRNAs generated from editing sites in wildtype animals, secondary siRNAs are generated from edited transcripts, suggesting ADARs antagonize only the first step of RNAi processing. We show that ADARs interfere with the efficacy of exogenous RNAi in vivo, probably to prevent trans-silencing, and have indications that ADR-2 binding to the dsRNA is needed for the efficient prevention of RNAi. This work sheds light on how the RNA editing process protects self-produced dsRNAs from aberrant recognition by the immune processes in the cell and from by-product degradation.
Conflict of interest statement
declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



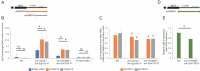
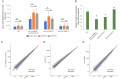
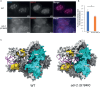
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
