Autophagy and Bacterial infections
- PMID: 40910070
- PMCID: PMC12407897
- DOI: 10.1080/27694127.2025.2542904
Autophagy and Bacterial infections
Abstract
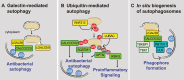
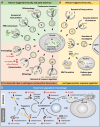
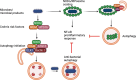
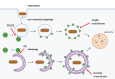
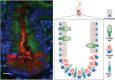
Autophagy is an evolutionarily conserved cellular process that is prominent during bacterial infections. In this review article, we discuss how direct pathogen clearance via xenophagy and regulation of inflammatory products represent dual functions of autophagy that coordinate an effective antimicrobial response. We detail the molecular mechanisms of xenophagy, including signals that indicate the presence of an intracellular pathogen and autophagy receptor-mediated cargo targeting, while highlighting pathogen counterstrategies, such as bacterial effector proteins that inhibit autophagy initiation or exploit autophagic membranes for replication. Pathways that are related to autophagy, including LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP) and conjugation of ATG8 to single membranes (CASM), are expanding the role of autophagy in antimicrobial defense beyond traditional double-membrane autophagosomes. Examination of Crohn disease-associated genes links impaired autophagy to inflammation and defective bacterial handling. We propose emerging concepts, such as effector-triggered immunity, where autophagy inhibition by pathogens triggers inflammatory defenses and discusses the therapeutic potential of modulating autophagy in infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Autophagy; CASM; Crohn disease; LC3 associated phagocytosis; bacteria; xenophagy.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
