Persistent Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) Infection in the Placenta of Pregnant Women
- PMID: 40910358
- PMCID: PMC12412083
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.70585
Persistent Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) Infection in the Placenta of Pregnant Women
Abstract
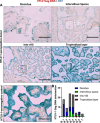
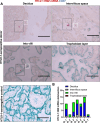
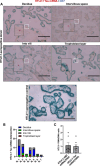
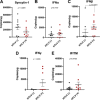
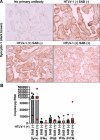
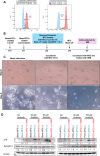
Mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) is the primary route of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infection. Although formula feeding reduces breastfeeding-associated transmission, MTCT still occurs, implicating pregnancy or delivery as key transmission windows. In this study, placental tissues from nine HTLV-1-positive mothers were analyzed using DNA/RNAscope, revealing low HTLV-1 DNA and RNA levels and a low RNA/DNA ratio, consistent with latent infection in the placenta and potentially explaining the low MTCT rate. Elevated interferon (IFN)-β levels were observed in infected placentas compared to seronegative controls, while IFNα, IFNγ, and IFITM expression remained unchanged. Concurrently, sustained IFNβ expression in infected placentas suggests its dual roles in HTLV-1 pathogenesis: suppressing viral replication while potentially disrupting placental homeostasis through chronic inflammation. In vitro modeling using BeWo cells or primary trophoblasts cocultured with HTLV-1-infected MT-2 cells demonstrated syncytin-1-mediated viral entry, confirmed by HTLV-1 p19 detection in both trophoblasts. Of note, HTLV-1 transmission was abolished by a syncytin-1-specific fusion inhibitor HRB1, underscoring syncytin-1's essential role in cell-to-cell transmission of HTLV-1. Thus, this study identifies syncytin-1 as a therapeutic target to block vertical transmission and highlights the need to balance antiviral responses with placental integrity in HTLV-1 management.
Keywords: HERV‐W1 Env; HTLV‐1; IFNβ; placenta; spontaneous abortions; syncytin‐1.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Medical Virology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Carneiro‐Proietti A. B. F., Amaranto‐Damasio M. S., Leal‐Horiguchi C. F., et al., “Mother‐to‐Child Transmission of Human T‐Cell Lymphotropic Viruses‐1/2: What We Know, and What Are the Gaps in Understanding and Preventing This Route of Infection,” Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society 3, no. S1 (2014): S24–S29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ureta‐Vidal A., Angelin‐Duclos C., Tortevoye P., et al., “Mother‐to‐Child Transmission of Human T‐Cell‐Leukemia/Lymphoma Virus Type I: Implication of High Antiviral Antibody Titer and High Proviral Load in Carrier Mothers,” International Journal of Cancer 82, no. 6 (1999): 832–836. - PubMed
-
- Dal Fabbro M. M. F. J., Cunha R. V., Bóia M. N., et al., “Infecção Pelo HTLV 1/2: Atuação No Pré‐Natal Como Estratégia De Controle Da Doença No Estado De Mato Grosso Do Sul,” Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical 41, no. 2 (2008): 148–151. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

