Genetically determined body mass index is associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in polygenic and Mendelian randomization analyses
- PMID: 40910475
- PMCID: PMC12588556
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.70039
Genetically determined body mass index is associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in polygenic and Mendelian randomization analyses
Abstract
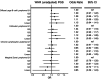
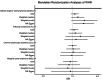
Obesity has been associated with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), but the evidence is inconclusive. We examined the association between genetically determined adiposity and four common NHL subtypes: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and marginal zone lymphoma, using eight genome-wide association studies of European ancestry (N = 10,629 cases, 9505 controls) and constructing polygenic scores for body mass index (BMI), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), and waist-to-hip ratio adjusted for BMI (WHRadjBMI). Higher genetically determined BMI was associated with an increased risk of DLBCL [odds ratio (OR) per standard deviation (SD) = 1.18, 95% confidence interval (95% CI): 1.05-1.33, p = .005]. This finding was consistent with Mendelian randomization analyses, which demonstrated a similar increased risk of DLBCL with higher genetically determined BMI (ORper SD = 1.12, 95% CI: 1.02-1.23, p = .03). No significant associations were observed with other NHL subtypes. Our study demonstrates a positive link between a genetically determined BMI and an increased risk of DLBCL, providing additional support for increased adiposity as a risk factor for DLBCL.
© 2025 International Agency for Research on Cancer; licensed by UICC and The Author(s). International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC. This article has been contributed to by U.S. Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
G. Salles is on the advisory board for Abbvie, Beigene, BMS, Genentech/Roche, Genmab, Incyte, Ipsen, Janssen, Kite/Gilead, Loxo/Lilly, Merck, Novartis, and Nurix; consults for Abbvie, Atbtherapeutics, Beigene, BMS, Debiopharm, Genentech/Roche, Genmab, Innate Pharma, Incyte, Ipsen, Kite/Gilead, Modex, Molecular Partners, Nordic, Nanovector, Orna Therapeutics, and Treeline; receives research support from Abbvie, Genentech, Genmab, Janssen, Ipsen, and Nurix; and is a shareholder of Owkin. T.M. Habermann is on the data monitoring committee for Seagen and Eli Lilly and receives research program support from Roche/Genentech, BMS, and Genmab. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U58 DP000807/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- HHSN261201000034C/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA134674/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201000140C/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA098122/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007033/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201000035C/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA134958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA165923/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA086862/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA167552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA148690/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201800016C/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES000260/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154643/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA062006/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA134919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000135/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201100004C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA098661/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201800016I/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092153/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201000035I/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA097274/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149445/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA257679/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA118444/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA042014/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

