Sensitivity of Different Clinical Outcome Measures in Assessing Adults With Becker Muscular Dystrophy: A 3-Year Natural History Study
- PMID: 40911807
- PMCID: PMC12413741
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000214071
Sensitivity of Different Clinical Outcome Measures in Assessing Adults With Becker Muscular Dystrophy: A 3-Year Natural History Study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Slow and highly variable disease progression in Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) stresses the need to develop sensitive outcome measures for clinical trials. We evaluated responsiveness of different outcome measures in adult patients with BMD over 3 years and explored if the sensitivity of outcome measures can be increased by selecting on phenotype or genotype.
Methods: Genetically confirmed patients with BMD were recruited via the Dutch Dystrophinopathy Database. Functional tests included North Star Ambulatory Assessment (NSAA), Timed Tests, Performance of the Upper Limb version 1.2, and pulmonary function yearly and echocardiography biennially. Mean changes and standardized response means (SRMs) were calculated per year. Outcome measures with SRM ≥0.80 were considered to have a high responsiveness to change. Two genetic subgroups-deletion of exons 45-47 and variants affecting the neuronal nitric oxide synthesis (nNOS) binding site-and one functional subgroup-NSAA between 10 and 32 at baseline-were analyzed separately.
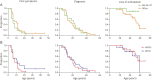
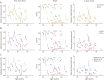
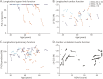
Results: Thirty-six patients with BMD were included (mean age 41.2 years, range 18.6-67.3, 27 ambulant at baseline). A high responsiveness was observed for the rise from floor velocity (RFFv) at 3-year follow-up (SRM -0.91, n = 16), while the SRMs for the other outcome measures were <0.8 at all time points. In the functional subgroup, a high responsiveness was observed for RFFv at 1-year follow-up (SRM -0.82, n = 10), along with 4-stair climb velocity (4SCv) (SRM -1.03, n = 11) and NSAA (SRM -0.82, n = 13) at 2-year follow-up. Genetic subgroups did not significantly differ in age at loss of ambulation (LoA). Upper limb and pulmonary function were preserved beyond LoA. Decline of cardiac function was independent of skeletal muscle function.
Discussion: RFFv was the only outcome measure sensitive to change at 3-year follow-up. Selecting on phenotype resulted in a high responsiveness for RFFv at 1-year follow-up and for 4SCv and NSAA at 2-year follow-up. NSAA could be performed in more participants compared with RFFv and therefore seems preferable in clinical trials for ambulant patients. Despite limitations in sample size, the results suggest that clinical trials in the ambulant population could be enriched by selecting on phenotype.
Conflict of interest statement
H.E. Kan reports research support from Philips Healthcare during the conduct of the study, and trial support from ImagingDMD-UF outside the submitted work; all reimbursements for H.E. Kan were received by the LUMC, and no personal financial benefits were received. P. Spitali reports funding from Edgewise Therapeutics for research; all reimbursements for P. Spitali were received by the LUMC, and no personal financial benefits were received. N. Ajmone Marsan received speaker fees from GE Healthcare, Philips Ultrasound, and Abbott Vascular; and received research grants from Pfizer, Alnylam, Astra Zeneca, Edwards Lifesciences, and Pie Medical through the Department of Cardiology. J.J.G.M. Verschuuren has been involved in MG research sponsored by the Princes Beatrix Fonds and Health Holland; is a member of the Target-to-B! consortium; is coinventor on patent applications based on MuSK-related research (the LUMC receives royalties for MuSK antibody assays); and has been involved in consultancies for Argenx, Alexion, and NMD Pharma (reimbursements were received by the LUMC). E.H. Niks discloses ad hoc consultancies for BioMarin, Entrada Therapeutics, Edgewise, Italfarmaco, Pfizer, Roche, Sarepta Therapeuticals, and Solid Bioscience, (all reimbursements were received by the LUMC; no personal financial benefits were received); reports receiving grants from Duchenne Parent Project, Prinses Beatrix Spierfonds, the European Union, Dutch Research Council, Spieren voor Spieren, and Pfizer; and has been site principal investigator for clinical trials conducted by BioMarin, Edgewise, Fibrogen, Italfarmaco, ML Bio, NS Pharma, Reveragen, Santhera Pharmaceuticals, Sarepta, Alexion, Janssen, and Argnx outside the submitted work. All other authors report no disclosures. Go to
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
