Development of Optimized Exatecan-Based Immunoconjugates with Potent Antitumor Efficacy in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 40912684
- PMCID: PMC12481485
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5c01184
Development of Optimized Exatecan-Based Immunoconjugates with Potent Antitumor Efficacy in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
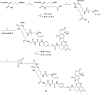
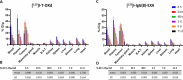
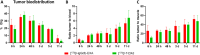
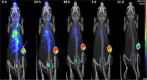
The prognosis of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer has significantly improved with the advent of anti-HER2 therapies, especially antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). In this field, ADCs, like trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd), using camptothecin analogs, represent a promising strategy. However, T-DXd can induce resistance and serious adverse effects, potentially driven by a non-specific Fcγ receptor-mediated endocytosis. Here, we report the development of novel HER2-targeting conjugates, using the camptothecin derivative exatecan and a linker optimized to control hydrophobicity. Three formats were evaluated: a high drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) 8 IgG-based ADC (IgG(8)-EXA), and two DAR 4 Fc-free constructs (Mb(4)-EXA and Db(4)-EXA). Thus, IgG(8)-EXA and Mb(4)-EXA displayed potent, specific cytotoxicity against HER2-positive breast cancer cells and strong antitumor activity in vivo. Notably, IgG(8)-EXA exhibited a favorable pharmacokinetic profile, despite its high DAR, supporting the potential of this drug-linker design. These two conjugates represent promising candidates for further preclinical development.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

