Molecularly matched targeted therapies plus radiotherapy in glioblastoma: the phase 1/2a N2M2 umbrella trial
- PMID: 40913172
- PMCID: PMC12532562
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-025-03928-9
Molecularly matched targeted therapies plus radiotherapy in glioblastoma: the phase 1/2a N2M2 umbrella trial
Abstract
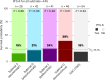
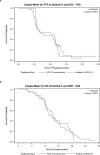
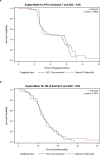
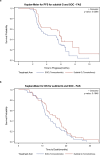
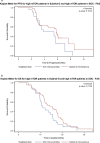
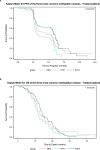
Advances in molecular understanding and diagnostic precision of glioblastoma enable the identification of key genetic alterations in a timely manner and, in principle, allow treatments with targeted compounds based on molecular markers. Here we report the results of the phase 1/2 umbrella trial NCT Neuro Master Match (N2M2), which evaluated targeted treatments in 228 patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma without O6-methylguanine DNA-methyltransferase promoter hypermethylation. Stratification for treatment was conducted by a trial-specific molecular tumor board across five subtrials, each evaluating a targeted therapy-alectinib, idasanutlin, palbociclib, vismodegib or temsirolimus-selected according to the best-matching molecular alteration. Patients without matching alterations were randomized between subtrials without strong biomarkers using atezolizumab and asunercept, and the standard of care (SOC), temozolomide. All received radiotherapy. The primary endpoints were dose-limiting toxicities (phase 1) and progression-free survival at 6 months (PFS-6; phase 2). Secondary endpoints included safety and tolerability, as well as overall survival (OS). The subtrials for alectinib and vismodegib did not open as they did not have matching patients. The idasanutlin subtrial (n = 9) was terminated early at the discretion of the manufacturing company. The temsirolimus subtrial (n = 46) demonstrated a PFS-6 of 39.1% and median OS of 15.4 months in patients with activated mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling compared to a PFS-6 at 18.5% in the SOC group (n = 54), meeting the primary endpoint. The atezolizumab (n = 42), asunercept (n = 26) and palbociclib (n = 41) subtrials did not meet the primary endpoint for efficacy. The safety signals of N2M2 match prior experiences with the drugs in quality and quantity; no relevant negative interaction with the parallel radiotherapy was noted. The results of the N2M2 trial support further investigation of temsirolimus in addition to radiotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with activated mTOR signaling. ClinicalTrials.gov registration: NCT03158389 .
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: W.W. declares consulting fees from Enterome, GSK and Servier. He received trial support with drugs from Apogenix, Pfizer and Roche. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

