Supporting decision making for individuals living with dementia and their care partners with knowledge translation: An umbrella review
- PMID: 40915983
- PMCID: PMC12414729
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70636
Supporting decision making for individuals living with dementia and their care partners with knowledge translation: An umbrella review
Abstract
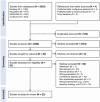
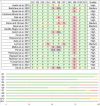
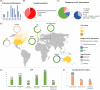
Living with dementia requires decision making about numerous topics including daily activities and advance care planning (ACP). Both individuals living with dementia and care partners require informed support for decision making. We conducted an umbrella review to assess knowledge translation (KT) interventions supporting decision making for individuals living with dementia and their informal care partners. Four databases were searched using 50 different search terms, identifying 22 reviews presenting 32 KT interventions. The most common KT decision topic was ACP (N = 21) which includes advanced care directives, feeding options, and placement in long-term care. The majority of KT interventions targeted care partners only (N = 16), or both care partners and individuals living with dementia (N = 13), with fewer interventions (N = 3) targeting individuals living with dementia. Overall, our umbrella review offers insights into the beneficial impacts of KT interventions, such as increased knowledge and confidence, and decreased decisional conflicts. HIGHLIGHTS: Knowledge translation (KT) helps people with dementia and caregivers make decisions. Our umbrella review investigated whether KT interventions helped decision making. KT interventions were beneficial, with advance care planning being the main topic. Thirteen (41%) of the 32 KT interventions were found to be freely accessible online. We recommend the creation of a KT toolkit to guide topic-specific decision making.
Keywords: care partner; decision making; individual living with dementia; knowledge translation.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no financial, personal, or competing interests/conflicts.
Figures
Update of
-
Supporting decision making for individuals living with dementia and their care partners with knowledge translation: an umbrella review.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 9:2024.09.17.24312581. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.17.24312581. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Sep;21(9):e70636. doi: 10.1002/alz.70636. PMID: 39371149 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Kurz AF. What is vascular dementia? Int J Clin Pract Suppl 2001:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Mixed dementia. Alzheimer Society of Canada . n.d. accessed April 22, 2024. https://alzheimer.ca/en/about‐dementia/other‐types‐dementia/mixed‐dementia
-
- Global status report on the public health response to dementia . World Health Organization; 2021.
-
- World failing to address dementia challenge n.d. accessed April 24, 2024. https://www.who.int/news/item/02‐09‐2021‐world‐failing‐to‐address‐dement...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- Courtois Foundation
- VAST Health Research Training to Address Vascular Contributions to Cognitive Decline, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Training Grant: Health Research Training Platform
- Consortium canadien en neurodégénérescence associée au vieillissement
- Canadian Institutes of Health Research Operating Grant: BHCIA: Knowledge Synthesis and Mobilization Grants - VCI
- Fonds de Recherche du Québec - Santé
- T32 NS131178/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Vascular Training Platform (VAST) summer student project
- Vascular Training Platform (VAST) Health Research Training Program Doctoral Award
- Vascular Training Platform (VAST) Postdoctoral fellowship
- National Institutes of Health Training grant
- Enhancing Patient Engagement in the Vascular Contributions to Cognitive Decline Training Platform, Canadian Institutes of Health Research
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

