miR-9-5p alleviates the development of abdominal aortic aneurysm by regulating the differentiation of CD4+IL-10+T cells via targeting the crosstalk between Nrf2 and NF-κB signaling pathways
- PMID: 40917297
- PMCID: PMC12410872
- DOI: 10.55730/1300-0152.2754
miR-9-5p alleviates the development of abdominal aortic aneurysm by regulating the differentiation of CD4+IL-10+T cells via targeting the crosstalk between Nrf2 and NF-κB signaling pathways
Abstract
Background: Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), a gradual segmental dilatation of the abdominal aorta, is associated with a high mortality rate. The pathophysiological molecular mechanisms underlying AAA remain unclear. In recent years, changes in miRNA levels have been reported to be involved in the development and treatment of AAA. This study aimed to investigate the potential targets and underlying mechanisms of miR-9-5p in attenuating AAA progression by modulating the inflammatory response.
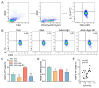
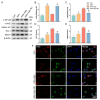
Materials and methods: Biochemical kits were used to measure the levels of inflammatory factors, antioxidant enzyme activity, and serum oxidative stress in normal and AAA model mice. miR-9-5p overexpression was achieved by transfecting miR-9-5p mimics into CD4+ T cells and administering an miR-9-5p agomir to the mice. The effect of miR-9-5p overexpression was evaluated by detecting the expression level of miR-9-5p in CD4+ T cells through qRT-PCR. The NF-κB/Nrf2 pathway levels were assessed using immunofluorescence, western blotting, and quantitative PCR. miR-9-5p expression was modulated by transfecting either miR-9-5p mimics or inhibitors, and the impact on CD4+IL-10+ T-cell differentiation was analyzed using flow cytometry.
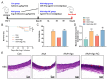
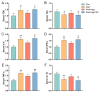
Results: Compared with that in the control group, miR-9-5p expression in CD4+ T cells from the peripheral blood of AAA model mice was decreased by 28%. In vivo, miR-9-5p intervention reduced AAA formation in model mice and markedly decreased serum oxidative stress damage and inflammatory factor levels. Furthermore, miR-9-5p intervention significantly increased miR-9-5p levels in CD4+ T cells both in vitro and in vivo, increased the proportion of CD4+IL-10+ T cells, suppressed NF-κB expression, and upregulated Nrf2 and its downstream antioxidant genes. Conversely, these therapeutic effects were abolished when an miR-9-5p inhibitor was administered.
Conclusions: By controlling the interaction between the Nrf2 and NF-κB signaling pathways, miR-9-5p mediates the differentiation of CD4+IL-10+ T cells and alleviates the development of AAA.
Keywords: Abdominal aortic aneurysm; CD4+ T cells; Nrf2; miR-9-5p; oxidative stress.
© TÜBİTAK.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Buzhong Yiqi decoction improves inflammation and oxidative damage in autoimmune thyroiditis by inhibiting apoptosis via the SIRT1-Mediated Nrf2/NF-κB axis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:119967. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119967. Epub 2025 May 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40360040
-
Upregulated miR-374a-5p drives psoriasis pathogenesis through WIF1 downregulation and Wnt5a/NF-κB activation.Cell Signal. 2024 Jul;119:111171. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111171. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38604345
-
ALOX5 regulates vascular smooth muscle cells pyroptosis to affect abdominal aortic aneurysm formation.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 9;15(1):29123. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14268-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40781109 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic surgery for elective abdominal aortic aneurysm repair.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 4;5(5):CD012302. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012302.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28471523 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
