Discovery of Potential Tyrosinase Inhibitors via Machine Learning and Molecular Docking with Experimental Validation of Activity and Skin Permeation
- PMID: 40918329
- PMCID: PMC12409553
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c04807
Discovery of Potential Tyrosinase Inhibitors via Machine Learning and Molecular Docking with Experimental Validation of Activity and Skin Permeation
Abstract
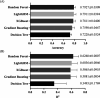
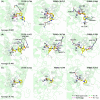
Tyrosinase, a copper-dependent oxidase, plays a critical role in melanin biosynthesis and is a target in skin-whitening cosmetics. Conventional inhibitors like arbutin and kojic acid are widely used but suffer from cytotoxicity, instability, and inconsistent efficacy, highlighting the need for safer, more effective alternatives. In this study, two ligand-based machine learning models were developed: one to predict the biological activity of compounds and the other to estimate specific pIC50 values. These models were employed to screen potential tyrosinase inhibitors from natural product libraries and FDA-approved drug databases. Subsequently, the molecules identified through machine learning screening were subjected to more precise multi tyrosinase-like structures molecular docking to refine the selection. We identified three top-ranking inhibitors, rhodanine-3-propionic acid, lodoxamide, and cytidine 5'-(dihydrogen phosphate), with strong binding affinities mediated by metal ion coordination and π-π interactions at the enzyme's active site. In vitro assays revealed that all three compounds exhibited higher inhibitory activity against mushroom tyrosinase compared to arbutin (IC50 = 38.37 mM), with rhodanine-3-propionic acid displaying the most potent inhibition (IC50 = 0.7349 mM). Furthermore, transdermal permeation experimental results confirmed that these compounds achieved markedly better skin permeability than commercial arbutin-based formulations, highlighting their potential as next-generation agents for inhibiting melanin production in cosmetic applications.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
