Broad-spectrum therapeutic potential of 4-phenylbutyrate in neurological and systemic diseases of viral and non-viral origin
- PMID: 40918526
- PMCID: PMC12408561
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1621590
Broad-spectrum therapeutic potential of 4-phenylbutyrate in neurological and systemic diseases of viral and non-viral origin
Abstract
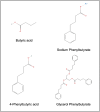
4-Phenylbutyrate (4-PBA), initially recognized for treating urea cycle disorders, has emerged as a potent therapeutic agent with broad-spectrum potential. As a chemical chaperone, 4-PBA modulates protein folding and reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress. 4-PBA has demonstrated efficacy in treating ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) infection and HSV-1-induced encephalitis, highlighting its potential as a novel anti-herpetic therapy. Beyond its antiviral properties, 4-PBA's therapeutic reach extends to neurological disorders linked to HSV-1 infection, including Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, Huntington's diseases, and primary open-angle glaucoma. Furthermore, 4-PBA shows promise in treating a diverse array of conditions beyond neurology. Its potential has been explored in atherosclerosis, Adriamycin-induced cardiac injury, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, rifamycin-induced liver injury, chronic kidney disease, diabetic nephropathy, NSAID-induced kidney injury, and chronic wound healing. This review synthesizes the multifaceted therapeutic potential of 4-PBA, emphasizing its role as a broad-spectrum agent capable of addressing a wide range of pathological conditions, particularly its role in combating HSV-1 and associated neurological disorders. The growing evidence suggests that 4-PBA may be a versatile and valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal against multiple diseases.
Keywords: 4-phenylbutyrate (4-PBA); Broadspectrum; herpes simplex virus; neurological disorders; therapeutic.
Copyright © 2025 Bobat, Wu, Tu, Kapoor, Sharma, Adams, Orameh, Yadavalli, Date and Shukla.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures






References
-
- Agarwal R. (2021). “Pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy,” in Chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. Arlington (VA): american diabetes association. Available online at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK571720/.
-
- Alfahel L., Argueti-Ostrovsky S., Barel S., Ali Saleh M., Kahn J., Azoulay-Ginsburg S., et al. (2022). 4-Phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) derivatives prevent SOD1 amyloid aggregation in vitro with no effect on disease progression in SOD1-ALS mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (16), 9403. 10.3390/ijms23169403 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

