Bis[1,2-bis-(4-fluoro-phen-yl)ethyl-ene-1,2-di-thiol-ato(1-)]nickel(II)
- PMID: 40918569
- PMCID: PMC12412703
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025007303
Bis[1,2-bis-(4-fluoro-phen-yl)ethyl-ene-1,2-di-thiol-ato(1-)]nickel(II)
Abstract
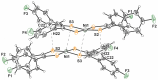
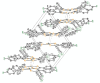
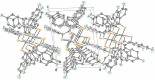
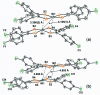
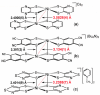
The crystal structure of the title compound, [Ni(C14H8F2S2)2] (I), reveals averaged S-C [1.708 (2) Å] and C-Cchelate [1.395 (4) Å] bond lengths that are consistent with radical monoanionic ligands paired with a divalent Ni2+ ion. Mol-ecules of I associate as dyads via inter-molecular Ni⋯S close contacts of 3.396 (2) Å. This close association is enabled by a bending of both di-thiol-ene ligands to the same side and away from the NiS4 planar inter-ior such that the angle between the seven atom mean planes defined by each NiS2C2 ring and the first C atom of each aryl substituent is 22.91 (8)°. These dyads form sheets in the bc plane that are held together in part by inter-molecular C-H⋯F hydrogen bonds of 2.47 (4) Å.
Keywords: C—H→F hydrogen bonds; crystal structure; dithiolene; electron-withdrawing; nickel; radical monoanion.
© Donahue et al. 2025.
Figures




References
-
- Artizzu, F., Espa, D., Marchiò, L., Pilia, L., Serpe, A. & Deplano, P. (2022). Inorg. Chim. Acta531, 120731.
-
- Arumugam, K., Bollinger, J. E., Fink, M. & Donahue, J. P. (2007). Inorg. Chem.46, 3283–3288. - PubMed
-
- Batsanov, S. S. (2001). Inorg. Mater.37, 871–885.
-
- Bigoli, F., Chen, C.-T., Wu, W.-C., Deplano, P., Mercuri, M. L., Pellinghelli, M. A., Pilia, L., Pintus, G., Serpe, A. & Trogu, E. F. (2001). Chem. Commun. pp. 2246–2247. - PubMed
-
- Bruker (2024). APEX5 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
