iMer, a naturally occurring MERTK splice variant, binds to GAS6 to decrease platelet activation and thrombus formation
- PMID: 40918742
- PMCID: PMC12412404
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bvth.2025.100078
iMer, a naturally occurring MERTK splice variant, binds to GAS6 to decrease platelet activation and thrombus formation
Abstract
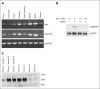
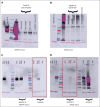
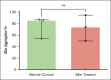
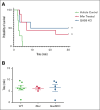
Unopposed platelet activation can be associated with pathologic thrombosis. An intact growth arrest-specific gene 6 (GAS6)/Mer receptor tyrosine kinase (MERTK) signaling pathway contributes importantly to potentiating platelet activation triggered by molecular agonists ex vivo and thrombus stabilization in vivo. We describe, herein, the inhibition of platelet function and stable thrombus formation conferred by iMer, a naturally occurring MERTK splice variant, that acts as a GAS6 decoy receptor and decreases phosphorylation of MERTK. Human and murine platelets incubated with this truncated protein demonstrate reduced activation in ex vivo assays including aggregometry (similar to treatment with anti-GAS6 antibody), expression of P-selectin, spreading on collagen, and accumulation on collagen at a venous shear rate. Wild-type C57BL/6 mice treated with iMer had improved survival in a collagen/epinephrine-induced pulmonary embolism model, without increase in tail bleeding time on preliminary analysis. Taken together, these findings confirm previous data suggesting the importance of GAS6-MERTK signaling in platelet activation and thrombus formation and highlighting the potential therapeutic implications of targeting this pathway as a means of treating or preventing thrombosis.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.D.P., D.K.G., and D.D. have stock in Meryx, Inc, a company developing novel anti-MERTK therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
