Implementation of LABSTER virtual lab in immunology for innovative teaching and improved learning in veterinary degree
- PMID: 40919042
- PMCID: PMC12411196
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1603469
Implementation of LABSTER virtual lab in immunology for innovative teaching and improved learning in veterinary degree
Abstract
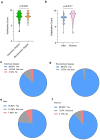
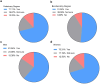
Virtual laboratories provide a risk-free environment for students to conduct experiments, particularly those involving hazardous materials or complex procedures. Previous studies have shown that gamified elements and interactive tools enhance the interest of students and promote active participation. In the case of Immunology in the veterinary degree, our prior observations indicate that veterinary students experience learning difficulties with topics related to molecules and effector functions of the immune system. This study aimed to investigate the utility of virtual laboratory simulations for teaching Immunology. For that purpose, cohorts of second-year veterinary students and third-year biochemistry students at the University of Extremadura were surveyed before and after the implementation of the LABSTER virtual lab in the Immunology course. The survey questions addressed their perceptions of virtual environments, prior computer knowledge, experiences with virtual platforms for learning, ethics, comparisons to traditional lab practices, and the perceived utility of virtual labs for their future careers. Gender differences were considered to determine potential variations in perceptions of virtual learning. Results indicated that veterinary students had no prior experience with LABSTER or similar virtual tools in other courses. Initially, nearly half of the students felt "unprepared" to use such tools. Notably, all students rated the experience using LABSTER virtual lab with an average of 7.5 ± 1.4 and 8.1 ± 1.8, in men and women, respectively. Indeed, most students perceived that LABSTER was useful for learning Immunology. Most students were hesitant about fully replacing traditional labs with virtual tools but found LABSTER beneficial for their future career skills. In conclusion, while virtual simulations are not a complete substitute for hands-on laboratory experiences, they may effectively help students develop practical skills and familiarize themselves with laboratory procedures and equipment. These findings highlight the potential of virtual labs as a complementary tool in veterinary education.
Keywords: LABSTER; biochemistry; immunology; innovative teaching and learning; veterinary; virtual lab; virtual simulator.
Copyright © 2025 Casado, Tarazona and Cordero.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could represent a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
A Comprehensive and Modality Diverse Cervical Spine and Back Musculoskeletal Physical Exam Curriculum for Medical Students.J Educ Teach Emerg Med. 2025 Jul 31;10(3):SG1-SG8. doi: 10.21980/J8RQ0N. eCollection 2025 Jul. J Educ Teach Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40766941 Free PMC article.
-
The educational effects of portfolios on undergraduate student learning: a Best Evidence Medical Education (BEME) systematic review. BEME Guide No. 11.Med Teach. 2009 Apr;31(4):282-98. doi: 10.1080/01421590902889897. Med Teach. 2009. PMID: 19404891
-
The effectiveness of using non-traditional teaching methods to prepare student health care professionals for the delivery of mental state examination: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Aug 14;13(7):177-212. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2263. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26455855
References
-
- Png CW, Goh LI, Chen YK, Yeo H, Liu H. A comparison of students’ preferences for face-to-face and online laboratory sessions: insights from students’ perception of their learning experiences in an immunology course. J Microbiol Biol Educ. (2024) 25:e0018123. doi: 10.1128/jmbe.00181-23, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gong T, Ding Y, Xiong Q. Web-based e-learning and virtual lab of human-artificial immune system. Pak J Pharm Sci. (2014) 27:729–34. PMID: - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

