RNA Modifications in Health and Disease
- PMID: 40919129
- PMCID: PMC12409077
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.70341
RNA Modifications in Health and Disease
Abstract
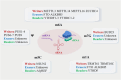
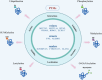
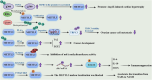
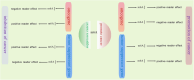
RNA modifications, including N6-methyladenosine (m6A), 5-methylcytosine, and pseudouridine, serve as pivotal regulators of gene expression with significant implications for human health and disease. These dynamic modifications influence RNA stability, splicing, translation, and interactions, thereby orchestrating critical biological processes such as embryonic development, immune response, and cellular homeostasis. Dysregulation of RNA modifications is closely associated with a variety of pathologies. This review systematically synthesizes recent advances in understanding how dynamic RNA modifications orchestrate health and disease. We critically review the m6A modifications, the most abundant RNA methylation, its association with diseases, and regulations by post translation. We evaluate three interconnected themes: disease mechanisms, where dysregulated m6A drives oncogenesis (e.g., METTL3-mediated hypermethylation in breast cancer) and contributes to neuropsychiatric/cardiovascular disorders; homeostatic functions, spanning embryogenesis (maternal-to-zygotic transition), tissue regeneration (YTHDF1 in muscle), and immune regulation; therapeutic frontiers, including enzyme-targeting strategies (FTO inhibitors, METTL3 stabilizers) and diagnostic approaches. Our analysis reveals that context-dependent RNA modification networks operate as biological "switches" whose dysregulation creates pathogenic cascades. We further propose a novel framework for targeting these networks using multiomics integration. This review establishes RNA modifications as central targets for precision medicine, while highlighting critical challenges in clinical translation that demand interdisciplinary collaboration.
Keywords: PTMs; RNA modifications; cancer; cardiovascular health; m6A methylation; neurodegenerative diseases.
© 2025 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Torres A. G., Batlle E., and Ribas de Pouplana L., “Role of tRNA Modifications in human Diseases, ” Trends in Molecular Medicine 20, no. 6 (2014): 306–314. - PubMed
-
- Cohn W. E., “Pseudouridine, a Carbon‐carbon Linked Ribonucleoside in Ribonucleic Acids: Isolation, Structure, and Chemical Characteristics, ” Journal of Biological Chemistry 235 (1960): 1488–1498. - PubMed
-
- Holley R. W., Apgar J., Everett G. A., et al., “Structure of a Ribonucleic Acid,” Science 147, no. 3664 (1965): 1462–1465. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
