Effects of yeast beta-1,3/1,6-glucans on nutrient digestibility, intestinal functionality, and immune and antioxidant variables in growing dogs submitted to spay or neutering surgery
- PMID: 40920667
- PMCID: PMC12416722
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0331843
Effects of yeast beta-1,3/1,6-glucans on nutrient digestibility, intestinal functionality, and immune and antioxidant variables in growing dogs submitted to spay or neutering surgery
Abstract
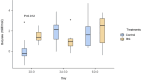
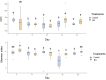
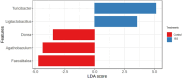
This study aimed to assess the impact of yeast beta-1,3/1,6-glucans (BG) on apparent digestibility coefficients (ADC) of nutrients, intestinal fermentative metabolites, fecal microbiota profile, and immune and antioxidant variables in puppies before and after surgical challenge. Two treatments were evaluated: control, without, and test, with oral supplementation of 65 mg/kg body weight/day of purified BG from Saccharomyces cerevisiae for 120 days. For this, 16 growing Beagle dogs were distributed in a completely randomized design (n = 8/treatment). On day 31, dogs were submitted to spay or neutering surgery. Diet ADC and fecal characteristics analyses were performed on days 55-60. Fecal (days 0, 15, 30, 34, and 60) and blood (days 0, 30, 34, and 60) samples were collected to evaluate intestinal fermentative metabolites, fecal IgA and microbiota, intestinal permeability, and immune and antioxidant variables. On day 80, all dogs were vaccinated for rabies and blood samples were collected on day 120 to determine antibody titers. The supplementation of BG promoted an increase in fecal IgA concentrations on day 15 (P < 0.05) and an increase in fecal concentrations of butyrate (P < 0.05) when day 30 minus day 0 were compared. Dogs of the BG group presented higher fecal concentrations of serotonin (day 15), spermidine (days 15, 30, and 34), and a reduction in tyramine, histamine, and cadaverine on day 60 (P < 0.001). BG consumption promoted an increase in richness and a clear differentiation in the fecal microbiota profile on days 34 and 60 (P < 0.05). BG group also presented an increase in fecal Faecalibacterium, Blautia, and Turicibacter on day 34 (P < 0.05). Reduced glutathione and catalase activities were higher in the BG group (P < 0.05), regardless of the day. In conclusion, the supplementation of BG does not alter the ADC of nutrients, beneficially modulates the intestinal functionality, and stimulates the activity of antioxidant enzymes in growing dogs submitted to a surgical challenge.
Copyright: © 2025 de Souza et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
Thaila Cristina Putarov is a Biorigin employee and reviewed the manuscript. She had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or first preparation of the manuscript. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of yeast-enriched functionalized canola meal supplementation on apparent total tract macronutrient digestibility and fecal characteristics, fecal microbiota, and immune function of healthy adult dogs.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae224. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae224. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39101402 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Bacillus coagulans (GBI-30, 6086) supplementation on apparent total tract nutrient digestibility and the fecal characteristics and metabolites, immunity, and microbiota of healthy adult dogs.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf251. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf251. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40831181
-
Effects of live Bacillus pumilus SG154 or a Lacticaseibacillus paracasei 327 postbiotic on apparent total tract nutrient digestibility and the immune function and fecal characteristics, metabolites, and microbiota of healthy adult dogs.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf231. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf231. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40685326
-
NTP Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity Technical Report on the Prenatal Development Studies of 2-((1-(4-Phenoxyphenoxy)propan-2-yl)oxy)pyridine (CASRN 95737-68-1) in Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley® SD®) Rats and New Zealand White (Hra:NZW SPF) Rabbits: DART Report 07 [Internet].Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Jan. Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Jan. PMID: 35593777 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Antioxidants for preventing and reducing muscle soreness after exercise.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 14;12(12):CD009789. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009789.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29238948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Topol I, Kamyshny A. Study of expression of TLR2, TLR4 and transcription factor NF-κB structures of galt of rats in the conditions of the chronic social stress and modulation of structure of intestinal microflora. Georgian Med News. 2013;115–22. - PubMed
-
- Souza RBMS, Soares NMM, Bastos TS, Kaelle GCB, de Oliveira SG, Félix AP. Effects of dietary supplementation with a blend of functional oils to fecal microbiota, and inflammatory and oxidative responses, of dogs submitted to a periodontal surgical challenge. Animal Feed Sci Tech. 2023;295:115527. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2022.115527 - DOI
-
- Li J, Li DF, Xing JJ, Cheng ZB, Lai CH. Effects of beta-glucan extracted from Saccharomyces cerevisiae on growth performance, and immunological and somatotropic responses of pigs challenged with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. J Anim Sci. 2006;84(9):2374–81. doi: 10.2527/jas.2004-541 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

