RNA-binding proteins mediate the maturation of chromatin topology during differentiation
- PMID: 40921733
- PMCID: PMC12431861
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-025-01735-5
RNA-binding proteins mediate the maturation of chromatin topology during differentiation
Abstract
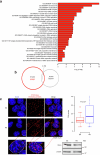
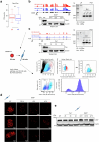
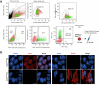
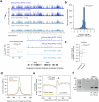
Topologically associating domains (TADs) and chromatin architectural loops impact promoter-enhancer interactions, with CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) defining TAD borders and loop anchors. TAD boundaries and loops progressively strengthen upon embryonic stem (ES) cell differentiation, underscoring the importance of chromatin topology in ontogeny. However, the mechanisms driving this process remain unclear. Here we show a widespread increase in CTCF-RNA-binding protein (RBP) interactions upon ES to neural stem (NS) cell differentiation. While dispensable in ES cells, RBPs reinforce CTCF-anchored chromatin topology in NS cells. We identify Pantr1, a non-coding RNA, as a key facilitator of CTCF-RBP interactions, promoting chromatin maturation. Using acute CTCF degradation, we find that, through its insulator function, CTCF helps maintain neuronal gene silencing in NS cells by acting as a barrier to untimely gene activation during development. Altogether, we reveal a fundamental mechanism driving developmentally linked chromatin structural consolidation and the contribution of this process to the control of gene expression in differentiation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


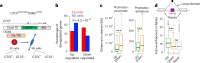
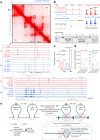
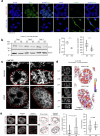
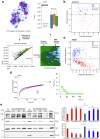
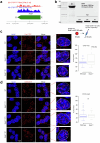
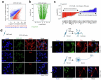
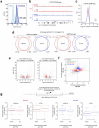
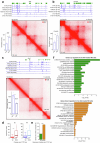
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Dioscuri Grant UMO-2018/01/H/NZ4/00001/Narodowe Centrum Nauki (National Science Centre)
- OPUS22 UMO-2021/43/B/NZ2/02934/Narodowe Centrum Nauki (National Science Centre)
- Sonata Bis 11 UMO-2021/42/E/NZ2/00392/Narodowe Centrum Nauki (National Science Centre)
- OPUS17 UMO-2019/33/B/NZ2/02437/Narodowe Centrum Nauki (National Science Centre)
- Grant Dioscuri UMO-2018/01/H/NZ4/00001/Narodowe Centrum Nauki (National Science Centre)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

