Multiancestry brain pQTL fine-mapping and integration with genome-wide association studies of 21 neurologic and psychiatric conditions
- PMID: 40921788
- PMCID: PMC12425806
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02291-2
Multiancestry brain pQTL fine-mapping and integration with genome-wide association studies of 21 neurologic and psychiatric conditions
Abstract
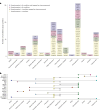
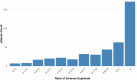
To understand shared and ancestry-specific genetic control of brain protein expression and its ramifications for disease, we mapped protein quantitative trait loci (pQTLs) in 1,362 brain proteomes from African American, Hispanic/Latin American and non-Hispanic white donors. Among the pQTLs that multiancestry fine-mapping MESuSiE confidently assigned as putative causal pQTLs in a specific population, most were shared across the three studied populations and are referred to as multiancestry causal pQTLs. These multiancestry causal pQTLs were enriched for exonic and promoter regions. To investigate their effects on disease, we modeled the 858 multiancestry causal pQTLs as instrumental variables using Mendelian randomization and genome-wide association study results for neurologic and psychiatric conditions (21 traits in participants with European ancestry, 10 in those with African ancestry and 4 in Hispanic participants). We identified 119 multiancestry pQTL-protein pairs consistent with a causal role in these conditions. Remarkably, 29% of the multiancestry pQTLs in these pairs were coding variants. These results lay an important foundation for the creation of new molecular models of neurologic and psychiatric conditions that are likely to be relevant to individuals across different genetic ancestries.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: A.I.L. serves as a consultant to Cognito, Asha Therapeutics, NextSense and Cognition Therapeutics. D.M.D., A.I.L. and N.T.S. are cofounders, employees, consultants and/or shareholders of EmTheraPro. D.M.D. and N.T.S. are cofounders of ARCProteomics. N.T.S. is a cofounder of Stitch-Rx. T.S.W. is a cofounder of revXon. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 AG072975/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- IK4 BX005219/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 AG061800/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG053960/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057911/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG071170/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036547/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG088425/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG075827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG079170/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX005686/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AG065187/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG061356/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG072120/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS072026/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

