Cerebral Venous Thrombosis:Current Status and Challenges
- PMID: 40923133
- PMCID: PMC12417975
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.70844
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis:Current Status and Challenges
Abstract
Background: Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) is a stroke type that primarily affects young individuals, with various risk factors and complex mechanisms. It accounts for 0.5% to 3% of all stroke cases and can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
Objective: This review aims to classify the etiology of CVT, assess its impact on prognosis, and evaluate the best treatment approaches. It also analyzes current issues in CVT management and proposes future directions for treatment.
Methods: A comprehensive review of the literature on CVT, focusing on risk factors, treatment strategies, and outcomes. The impact of anticoagulation therapy and endovascular interventions is examined.
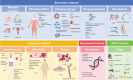
Results: This review examines the various risk factors associated with CVT, including female-specific conditions, infections, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and mechanical triggers. It highlights the impact of these factors on the prognosis and outcomes of CVT. The effectiveness of anticoagulation therapy, both traditional and with direct oral anticoagulants, is discussed, along with the role of endovascular therapy in severe cases. The review also identifies current challenges in CVT management, such as incomplete thrombus clearance and the lack of standardized evaluation criteria for recanalization.
Conclusion: Further research is needed to optimize CVT management, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.
Keywords: cerebral venous thrombosis; prognosis; risk factor; sinus thrombosis; treatment.
© 2025 The Author(s). Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

