Position-correlated biphoton wavefront sensing for quantum adaptive imaging
- PMID: 40925903
- PMCID: PMC12420783
- DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-02024-4
Position-correlated biphoton wavefront sensing for quantum adaptive imaging
Abstract
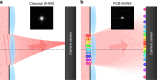
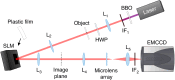
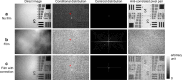
Quantum imaging with spatially entangled photons offers advantages such as enhanced spatial resolution, robustness against noise, and counterintuitive phenomena, while a biphoton spatial aberration generally degrades its performance. Biphoton aberration correction has been achieved by using classical beams to detect the aberration source or scanning the correction phase on biphotons if the source is unreachable. Here, a new method named position-correlated biphoton Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensing is introduced, where the phase pattern added on photon pairs with a strong position correlation is reconstructed from their position centroid distribution at the back focal plane of a microlens array. Experimentally, biphoton phase measurement and adaptive imaging against the disturbance of a plastic film are demonstrated. This single-shot method is a more direct and efficient approach toward quantum adaptive optics, suitable for integration into quantum microscopy, remote imaging, and communication.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang, Z. S. et al. Entanglement-based quantum information technology: a tutorial. Adv. Opt. Photonics16, 60–162 (2024).
-
- Moreau, P. A. et al. Imaging with quantum states of light. Nat. Rev. Phys.1, 367–380 (2019).
-
- Defienne, H. et al. Advances in quantum imaging. Nat. Photonics18, 1024–1036 (2024).
-
- Pittman, T. B. et al. Optical imaging by means of two-photon quantum entanglement. Phys. Rev. A52, R3429–R3432 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Lemos, G. B. et al. Quantum imaging with undetected photons. Nature512, 409–412 (2014). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

