Characterization of the extrinsic and intrinsic signatures and therapeutic vulnerability of small cell lung cancers
- PMID: 40925909
- PMCID: PMC12420805
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-025-02378-6
Characterization of the extrinsic and intrinsic signatures and therapeutic vulnerability of small cell lung cancers
Abstract
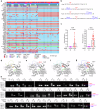
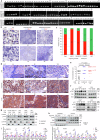
Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), an aggressive neuroendocrine tumor strongly associated with exposure to tobacco carcinogens, is characterized by early dissemination and dismal prognosis with a five-year overall survival of less than 7%. High-frequency gain-of-function mutations in oncogenes are rarely reported, and intratumor heterogeneity (ITH) remains to be determined in SCLC. Here, via multiomics analyses of 314 SCLCs, we found that the ASCL1+/MKI67+ and ASCL1+/CRIP2+ clusters accounted for 74.38% of the 190,313 SCLC cancer cells from 39 patients, with the ASCL1+SOX1+ stem-like cell cluster across SCLC subtypes. The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules were expressed at low levels in six and high levels in five cancer cell clusters and were inversely associated with the KI67 expression level. Abnormal splicing of mRNAs was a feature of SCLC, with focal adhesion kinase (FAK) splicing variants identified in 119 (77.3%) of 154 patients. FAK variants exhibited elevated kinase activity, were associated with the worst prognosis, and were sensitive to FAK inhibitors in patient-derived organoids and xenograft models. Eleven high-frequency mutations were identified in addition to TP53 and RB1, and smoking status and tumor stage did not affect microbiota variance in SCLC. Taken together, our data further revealed the complicated ITH and discovered that FAK splicing variants represent high-frequency gain-of-function alterations in oncogene in SCLC and potential therapeutic targets for this recalcitrant cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Sung, H. et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.71, 209–249 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

