The Anti-Leukemic Potential of Curcumin in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
- PMID: 40927046
- PMCID: PMC12415269
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.70852
The Anti-Leukemic Potential of Curcumin in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Abstract
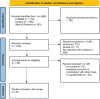
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), a myeloproliferative neoplasm, is characterized by the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene, which results in constitutive tyrosine kinase activity. While tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have significantly improved CML outcomes, resistance and the persistence of leukemic stem cells remain major clinical challenges. Curcumin, a natural polyphenol derived from Curcuma longa, has demonstrated potential anticancer properties. This review explores curcumin's effects on CML cell lines, focusing on its mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential. A systematic literature search was conducted in December 2024 across PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases, following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. The review included original in vitro studies examining curcumin's anti-leukemic effects on human CML cell lines. Data was extracted and synthesized narratively due to methodological variability. Of 869 screened articles, 21 in vitro studies met the inclusion criteria. Curcumin inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in CML cell lines, particularly K562. Key mechanisms included inhibition of protein kinase C alpha (PKCα), Wilms' tumor 1 (WT1), BCR-ABL1 signaling, and histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) expression, as well as modulation of microRNA-21 (miR-21), phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), and suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 and 3 (SOCS1/3) pathways. Curcumin also triggered cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase and promoted autophagy and mitochondrial dysfunction. Notably, curcumin derivatives such as pentagamavunon-1 (PGV-1) and compound 1206 (C1206) displayed enhanced potency and overcame resistance in imatinib-resistant CML cells. Curcumin demonstrates multi-targeted anti-leukemic activity in vitro, disrupting oncogenic signaling, epigenetic regulation, and redox balance in CML cells. Its ability to sensitize resistant cells and enhance apoptotic pathways positions it as a promising adjunct to current CML therapies. However, clinical translation requires further investigation to overcome pharmacokinetic limitations and validate efficacy in vivo.
Keywords: apoptosis; cell proliferation; chronic myeloid leukemia; curcumin; drug resistance.
© 2025 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad, B. , Naikoo M. I., Jaleel H., et al. 2017. “Signaling Pathways of Anticancer Plants: Action and Reaction.” Anticancer Plants: Clinical Trials and Nanotechnology 3: 303–322.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

