PRMT1-Mediated PARP1 Methylation Drives Lung Metastasis and Chemoresistance via P65 Activation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 40927753
- PMCID: PMC12415337
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0854
PRMT1-Mediated PARP1 Methylation Drives Lung Metastasis and Chemoresistance via P65 Activation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
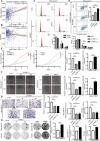
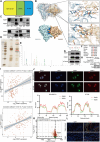
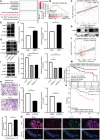
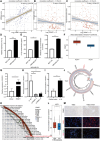
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive breast cancer subtype, characterized by a high propensity for metastasis, poor prognosis, and limited treatment options. Research has demonstrated a substantial correlation between the expression of protein arginine N-methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) and enhanced proliferation, metastasis, and poor outcomes in TNBC. However, the specific role of PRMT1 in lung metastasis and chemoresistance remains unclear. Single-cell RNA sequencing coupled with bioinformatics analysis was employed to identify pertinent genes within metastatic TNBC samples. Functional assays, including cell cycle, apoptosis, wound healing, Transwell migration, colony formation, and Cell Counting Kit-8 Assay (CCK-8), were conducted to evaluate the role of PRMT1. The interaction between PRMT1 and PARP1 was validated by mass spectrometry (MS) and immunoprecipitation. Downstream signaling pathways were explored, with a focus on P65 activation. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to quantify the effect of PRMT1 on interleukin-1β secretion. Our study identified a significant association between elevated PRMT1 expression and both lung metastasis and chemoresistance in TNBC. PRMT1 boosts TNBC cell growth, invasion, and lung metastasis. Additionally, high PRMT1 expression contributed to increased resistance to docetaxel in TNBC. Mechanistically, PRMT1 methylates PARP1. On the one hand, this methylation promotes the DNA damage repair ability of PAPA1. On the other hand, it in turn modulates the NF-κB signaling pathway. This modulation enhances the stemness of tumor cells and induces immune suppression within the tumor microenvironment, thereby exacerbating chemoresistance in TNBC. PRMT1 drives lung metastasis and chemoresistance in TNBC through PARP1 methylation and P65 activation. These findings position PRMT1 as a promising biomarker and therapeutic target to overcome resistance and limit metastatic progression in TNBC.
Copyright © 2025 Jinhui Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(1):12–49. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–263. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–132. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, Ma J, Gaudet MM, Newman LA, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Jemal A, Siegel RL. Breast cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(6):438–451. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

