Functional synapses between neurons and small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 40931078
- PMCID: PMC12571904
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09434-9
Functional synapses between neurons and small cell lung cancer
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Functional synapses between neurons and small cell lung cancer.Nature. 2025 Oct;646(8086):E17. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09638-z. Nature. 2025. PMID: 40973832 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
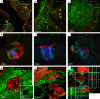
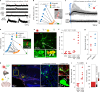
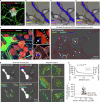
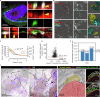
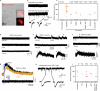
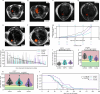
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a highly aggressive type of lung cancer, characterized by rapid proliferation, early metastatic spread, frequent early relapse and a high mortality rate1-3. Recent evidence has suggested that innervation has an important role in the development and progression of several types of cancer4,5. Cancer-to-neuron synapses have been reported in gliomas6,7, but whether peripheral tumours can form such structures is unknown. Here we show that SCLC cells can form functional synapses and receive synaptic transmission. Using in vivo insertional mutagenesis screening in conjunction with cross-species genomic and transcriptomic validation, we identified neuronal, synaptic and glutamatergic signalling gene sets in mouse and human SCLC. Further experiments revealed the ability of SCLC cells to form synaptic structures with neurons in vitro and in vivo. Electrophysiology and optogenetic experiments confirmed that cancer cells can receive NMDA receptor- and GABAA receptor-mediated synaptic inputs. Fitting with a potential oncogenic role of neuron-SCLC interactions, we showed that SCLC cells derive a proliferation advantage when co-cultured with vagal sensory or cortical neurons. Moreover, inhibition of glutamate signalling had therapeutic efficacy in an autochthonous mouse model of SCLC. Therefore, following malignant transformation, SCLC cells seem to hijack synaptic signalling to promote tumour growth, thereby exposing a new route for therapeutic intervention.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: H.C.R. received consulting and lecture fees from Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Vertex and Merck. H.C.R. received research funding from AstraZeneca and Gilead Pharmaceuticals. H.C.R. is a co-founder of CDL Therapeutics. R.K.T. is a founder of PearlRiver Bio (now part of Centessa), a shareholder of Centessa, a founder and shareholder of Epiphanes and a consultant to PearlRiver Bio and Epiphanes. R.K.T. has received research support from Roche. R.K.T. and J.S. are co-founders and shareholders of DISCO Pharmaceuticals. M.L.S. is a co-founder and was an advisor of PearlRiver Bio (now part of Centessa). M.L.S. received research funding from PearlRiver Bio (now part of Centessa). S.O.R. is a shareholder of NanoTag Biotechnologies. H.W. was a co-founder of Apogenix. J. George is a consultant to DISCO Pharmaceuticals and received honoraria from MSD and Boehringer Ingelheim. J. Brägelmann has received research funding from Bayer and travel grants from Merck and Bicycle Therapeutics. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
-
- Rudin, C. M., Brambilla, E., Faivre-Finn, C. & Sage, J. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers7, 3 (2021).
-
- Pan, C. & Winkler, F. Insights and opportunities at the crossroads of cancer and neuroscience. Nat. Cell Biol.24, 1454–1460 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

