The mTORC2 subunit RICTOR drives breast cancer progression by promoting ganglioside biosynthesis through transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms
- PMID: 40934285
- PMCID: PMC12425323
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003362
The mTORC2 subunit RICTOR drives breast cancer progression by promoting ganglioside biosynthesis through transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms
Abstract
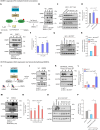
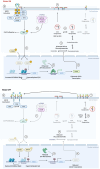
Sphingolipid and ganglioside metabolic pathways are crucial components of cell signaling, having established roles in cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration. However, regulatory mechanisms controlling sphingolipid and ganglioside biosynthesis in mammalian cells are less known. Here, we show that RICTOR, the regulatory subunit of mTORC2, regulates the synthesis of sphingolipids and gangliosides in human luminal breast cancer-specific MCF-7 and BT-474 cells through transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms. We observe that RICTOR regulates glucosylceramide levels by modulating the expression of UDP-Glucose Ceramide Glucosyl transferase (UGCG). We identify Zinc Finger protein X-linked (ZFX) as a RICTOR-responsive transcription factor whose recruitment to the UGCG promoter is regulated by DNA methyltransferase 1 and histone demethylase (KDM5A), which are known AKT substrates. We further demonstrate that RICTOR regulates the synthesis of GD3 gangliosides through ZFX and UGCG, and triggers the activation of the EGFR signaling pathway, thereby promoting tumor growth. In line with our findings in human cell culture and mouse models, we observe an elevated expression of RICTOR, ZFX, and UGCG in Indian luminal breast cancer tissues and in TCGA and METABRIC datasets. Together, we establish a key regulatory circuit, RICTOR-AKT-ZFX-UGCG-Ganglioside-EGFR-AKT, and elucidate its contribution to breast cancer progression.
Copyright: © 2025 Ansari et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Zhang X, Kiechle FL. Review: glycosphingolipids in health and disease. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2004;34(1):3–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

