Raloxifene solubility in supercritical CO2 and correlation of drug solubility via hybrid machine learning and gradient based optimization
- PMID: 40935865
- PMCID: PMC12426225
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-17642-6
Raloxifene solubility in supercritical CO2 and correlation of drug solubility via hybrid machine learning and gradient based optimization
Abstract
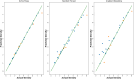
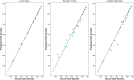
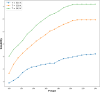
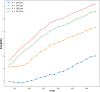
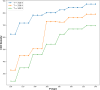
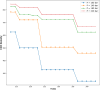
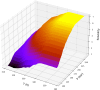
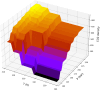
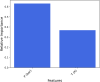
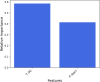
One of the problems with new medications is their poor water solubility that is possible to be addressed by using supercritical method. This study aims to predict the solubility of raloxifene and the density of supercritical CO2 using temperature and pressure as inputs to analyze the supercritical processing for production of drug nanoparticles. Three regression models, Extra Trees (ET), Random Forest (RF), and Gradient Boosting (GB) were proposed and optimized using Gradient-based optimization to predict density and solubility of drug. In predicting the density of supercritical CO₂, GB attained an R² value of 0.986, reflecting an excellent agreement between its estimates and the true measurements. The model exhibited an RMSE of 23.20, indicating high accuracy, with a maximum error of 33.06. Regarding the solubility of raloxifene, the ET model yielded the highest R-squared score of 0.949, indicating a good fit to the data. The model exhibited an RMSE of 0.41, with a maximum error of 0.90. Comparatively, the RF and GB models obtained slightly lower precision, for the solubility of raloxifene. The RF model exhibited an RMSE of 0.55, while the GB model had an RMSE of 0.72. The optimized models were found to be reliable in predicting solubility and density within the supercritical processing field.
Keywords: Drug computation; Extra trees; Gradient boosting; Machine learning; Process modeling; Random forest; Solubility.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Pu, S. & Hadinoto, K. Habit modification in pharmaceutical crystallization: A review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des.201, 45–66 (2024). - DOI
-
- Guillou, P., Marre, S. & Erriguible, A. Thermodynamic assessment of two-step nucleation occurrence in supercritical fluid. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 211, 106292 (2024). - DOI
-
- AravindKumar, P. et al. New solubility model to correlate solubility of anticancer drugs in supercritical carbon dioxide and evaluation with Kruskal–Wallis test. Fluid. Phase. Equilibria. 582, 114099 (2024). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

