Crucial roles of CircRNA-mediated autophagy in digestive cancer
- PMID: 40936702
- PMCID: PMC12420225
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1615306
Crucial roles of CircRNA-mediated autophagy in digestive cancer
Abstract
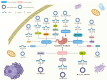
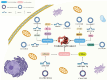
Digestive cancers are a significant global public health challenge due to their high incidence and mortality rates. Emerging research highlights the pivotal role of circular RNA (circRNA) and autophagy in the progression of digestive cancers. This review provides a summary of recent findings, showing that circRNA-mediated autophagy could either promote or suppress tumor development in esophageal, gastric, liver, pancreatic, and colorectal cancers. CircRNAs could regulate autophagy in digestive cancers by acting as competitive endogenous RNAs, influencing downstream target genes and signaling pathways. Dysregulated circRNAs contribute to tumor onset, progression, and chemoresistance by altering autophagy levels. Targeting specific circRNAs to modulate autophagy may offer potential as a diagnostic, prognostic biomarker, or therapeutic strategy for digestive cancers.
Keywords: autophagy; chemoresistance; circular RNA; digestive cancer; molecular mechanisms.
Copyright © 2025 Shi, Wei, Yang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

