IFIT3 activation significantly contributes to HIV-1-associated neurodegenerative disorder-mediated neuroinflammation
- PMID: 40936921
- PMCID: PMC12420264
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1532318
IFIT3 activation significantly contributes to HIV-1-associated neurodegenerative disorder-mediated neuroinflammation
Abstract
Introduction: The advent of effective combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) has significantly improved HIV-1 treatment, saving millions of lives. However, HAND remains a concern, particularly among aging individuals with HIV-1. The mechanisms underlying HAND are not well understood.
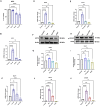
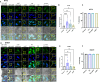
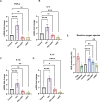
Methods: This study investigated the role of interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3 (IFIT3) and its upstream regulator, signal transducer, and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1), in HAND pathology. Using the SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line and HIV-infected humanized mice, we examined the effects of the cART drugs, HIV Tat protein, and HIV-1 virus on STAT1 and IFIT3 expression.
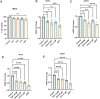
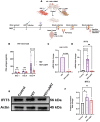
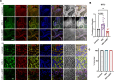
Results: The results showed that HIV-1 exposure significantly upregulated STAT1 and IFIT3, contributing to neuroinflammation.
Discussion: This study identified IFIT3 as a critical molecular marker for HAND, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target and offering new insights into disease pathology and treatment strategies.
Keywords: HAND; HIV; IFIT3; SH-SY5Y cells; STAT1; Tat protein; cART.
Copyright © 2025 Das, Sahoo, Roy, Xu, Galarza, Garza, Rodrigo, Duttaroy and Roy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . The Global Health Observatory (2022). Available online at: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/hiv-aids/data-on-the-size-of-th....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

