Ultrasound-guided percutaneous thermal and non-thermal ablation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 40937452
- PMCID: PMC12421398
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i34.108623
Ultrasound-guided percutaneous thermal and non-thermal ablation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Ultrasound-guided percutaneous thermal ablation has gained popularity as treatment for malignant hepatic tumors. It was first introduced as ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis comorbidity. Recently, this technique has also been used in the treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma for patients who are not eligible for surgical resection. There are several types of thermal ablation techniques. Radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation are two common methods that induce necrosis of the lesions. Irreversible electroporation is a relatively new non-thermal technique and is suitable in cases where thermal ablation would be ineffective or dangerous (e.g., malignant tumors close to vascular or biliary structures). Irreversible electroporation can induce tumoral necrosis without damage to vascular and biliary structures. The aim of this minireview was to describe the safety, efficacy, and clinical indications of these techniques in the treatment of patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma who are ineligible for surgery.
Keywords: Interventional ultrasonography; Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; Irreversible electroporation; Microwaves ablation; Percutaneous ablation; Radiofrequency ablation; Thermal ablation.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
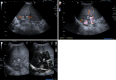
Figures

References
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL-ILCA Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. 2023;79:181–208. - PubMed
-
- Bergquist A, von Seth E. Epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;29:221–232. - PubMed
-
- Clements O, Eliahoo J, Kim JU, Taylor-Robinson SD, Khan SA. Risk factors for intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2020;72:95–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

