Enhancing Muscle Quality: Exploring Leucine and Whey Protein in Sarcopenic Individuals
- PMID: 40937507
- PMCID: PMC12426612
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.70060
Enhancing Muscle Quality: Exploring Leucine and Whey Protein in Sarcopenic Individuals
Abstract
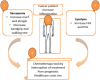
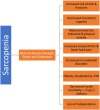
Background: Sarcopenia is characterised by a decline in the skeletal muscle mass with increasing age. This poses many challenges to the health and independence of older individuals. New and emerging studies have focused on supplementing leucine-enriched whey protein and resistance training in older adults to mitigate the effects of sarcopenia, including significant muscle mass loss.
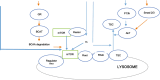
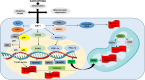
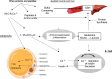
Methods: This study aimed to comprehensively analyse the current literature regarding the beneficial effects of leucine-enriched whey protein supplementation in older adults. This article systematically reviewed randomised controlled trials, longitudinal studies, and meta-analyses published between 2011 and 2024. The biochemical mechanisms underlying the anabolic properties of leucine, including its role in protein synthesis and mTOR signalling pathways, were explored to elucidate its potential to enhance muscle protein accretion.
Results: Findings from the reviewed studies indicate that the combined intervention of leucine-enriched whey protein supplementation and resistance training elicits favourable outcomes regarding increased lean muscle mass, muscle strength and physical performance in older adults with sarcopenia. The potential of leucine-enriched whey protein to mitigate muscle protein breakdown is discussed along with its potential synergistic effects with resistance exercise to optimise muscle adaptation. Future research directions, including investigations of optimal dosing regimens, long-term sustainability and potential contraindications, are proposed to enhance the precision and applicability of this intervention strategy.
Conclusion: Leucine-enriched whey protein supplementation combined with resistance training is beneficial in addressing sarcopenia in older adults. This review consolidates the current understanding of this intervention, highlights its potential benefits and provides insights for future research and clinical applications in geriatric muscle health.
Keywords: mTOR signalling pathway; muscle health; whey protein.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to report.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Malmstrom T. K. and Morley J. E., “SARC‐F: A Simple Questionnaire to Rapidly Diagnose Sarcopenia,” Journal of the American Medical Directors Association 14 (2013): 531–532. - PubMed
-
- Hanif H., Islam F., Khalid S., Hannan M. A., Aslam M., and Raza A., “Prevalence of Sarcopenia in Adults Having Diabetes Mellitus,” Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition 19 (2023): 41–49.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

