Identification of the Centrifugation-Caused Paralytic Impact on Neutrophils
- PMID: 40940760
- PMCID: PMC12427856
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14171350
Identification of the Centrifugation-Caused Paralytic Impact on Neutrophils
Abstract
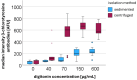
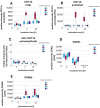
To investigate granulocytes under laboratory conditions, centrifugation steps are typically required for the isolation of neutrophil granulocytes from whole blood. However, only a few studies to date have addressed the direct effects of centrifugation itself on the functional state of neutrophils. This study aims to elucidate the mechanisms that contribute to the modification of granulocytes during centrifugation. We hypothesize that granules sustain morphological alterations during centrifugation, leading to the release of highly potent antimicrobial enzymes into the cytosol of the cells. Neutrophils were isolated from whole blood using different methods with and without centrifugation and analyzed by flow cytometry, ELISA, and mass spectrometry. Our findings demonstrate that intracellular granules incur damage during centrifugation, resulting in the presence of intragranular enzymes within the cytosol. Furthermore, the formation of the highly reactive hypochlorous acid (HOCl) as a consequence of centrifugation could be verified. The generation of intracellular HOCl may explain many of the alterations observed in neutrophils following centrifugation-based isolation, including modified surface antigen expression and altered responses to stimulation. In future studies, centrifugation steps during cell isolation should be avoided. The more time-consuming but gentler method of sedimentation is preferable and can be used as long as it is not necessary to obtain a highly purified neutrophil fraction.
Keywords: HOCl; Myeloperoxidase; centrifugation; granules; impairment; isolation; neutrophil functions; neutrophils; reactive oxygen species; surface antigen expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Blanter M., Cambier S., de Bondt M., Vanbrabant L., Pörtner N., Abouelasrar Salama S., Metzemaekers M., Marques P.E., Struyf S., Proost P., et al. Method Matters: Effect of Purification Technology on Neutrophil Phenotype and Function. Front. Immunol. 2022;13:820058. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.820058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

