Evolving Paradigms in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Personalized Approaches to Therapy Across Age and Risk Groups
- PMID: 40940920
- PMCID: PMC12427493
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17172824
Evolving Paradigms in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Personalized Approaches to Therapy Across Age and Risk Groups
Abstract
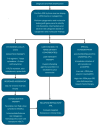
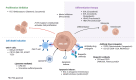
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive hematologic malignancy characterized by the clonal proliferation of myeloid precursors and rapid progression. Historically consisting of intensive chemotherapy, AML management has evolved significantly due to advances in molecular diagnostics and risk stratification. This review discusses current therapeutic paradigms in AML, emphasizing the growing role of personalized medicine across age and risk groups. For younger, fit patients, intensive regimens such as the "7 + 3" protocol remain the standard, often enhanced by targeted agents like FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) and IDH inhibitors. Older or unfit individuals benefit from low-intensity treatments such as hypomethylating agents combined with venetoclax, now considered a frontline standard of care. The use of liposomal chemotherapy (CPX-351), measurable residual disease (MRD) monitoring, and maintenance therapy further refine post-remission strategies. Emerging therapies, including menin inhibitors, antibody-drug conjugates, and immunotherapies like CAR-T cells and vaccines, offer additional options, especially in relapsed/refractory settings. This comprehensive review outlines the current landscape and future directions in AML therapy, emphasizing the transition toward individualized, mutation-driven treatment strategies.
Keywords: CPX-351; FLT3 inhibitors; IDH inhibitors; Menin inhibitors; acute myeloid leukemia; measurable residual disease; molecular profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Döhner H., Wei A.H., Appelbaum F.R., Craddock C., DiNardo C.D., Dombret H., Ebert B.L., Fenaux P., Godley L.A., Hasserjian R.P., et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022;140:1345–1377. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022016867. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khoury J.D., Solary E., Abla O., Akkari Y., Alaggio R., Apperley J.F., Bejar R., Berti E., Busque L., Chan J.K.C., et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia. 2022;36:1703–1719. doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01613-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous