PIAS1 Shapes a Tumor-Suppressive Microenvironment by Suppressing Immune Evasion in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 40941002
- PMCID: PMC12427710
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17172905
PIAS1 Shapes a Tumor-Suppressive Microenvironment by Suppressing Immune Evasion in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The SUMO E3 ligase PIAS1 (Protein Inhibitor of Activated STAT1) regulates pathways such as TGFβ signaling and has been implicated in multiple cancers. However, its role in the tumor microenvironment (TME), particularly in non-malignant stromal and immune cells, remains poorly understood. This study aimed to characterize the expression and functional relevance of PIAS1 within the TME of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
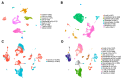
Methods: PIAS1 protein expression was assessed via immunohistochemistry (IHC) on OSCC tissue microarrays. Single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) datasets from OSCC tumors and normal tissues were analyzed to map cell-type-specific PIAS1 expression. Downstream effects were evaluated using differential gene expression, Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA), gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA), and cell-cell communication inference.
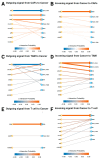
Results: IHC analysis revealed that higher stromal PIAS1 levels correlated with improved survival. scRNA-seq analysis showed an increase in the proportion of PIAS1-expressing cells across most stromal and immune cell populations within OSCC-derived tumors compared to their counterparts in adjacent normal tissue. However, when comparing PIAS1-positive cells, expression levels were significantly reduced in cancer cells, CAFs, TAMs, T cells, and endothelial cells within the TME. PIAS1-positive CAFs, TAMs, and T cells exhibited activation of apoptotic and tumor-suppressive pathways, while PIAS1-negative counterparts showed enrichment of immunosuppressive signaling and immune checkpoint expression. Cell-cell communication analyses indicated that PIAS1 fosters an immune-activated TME by promoting pro-inflammatory signaling, M1-like TAM polarization, and T cell activation.
Conclusions: PIAS1 expression in stromal and immune cells is associated with tumor-suppressive reprogramming of the OSCC microenvironment. These findings position PIAS1 as a potential modulator of anti-tumor immunity and candidate target for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: PIAS1; oral squamous cell carcinoma; single-cell RNA-seq; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Babu S., Manavalan M.J., Hifza Jasmine S., Krishnan M. Tumor microenvironment in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Implications for novel therapies. [(accessed on 27 May 2025)];Oral Oncol. Rep. 2024 12:100666. doi: 10.1016/j.oor.2024.100666. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772906024005120?ref=.... - DOI
-
- Puhr M., Hoefer J., Eigentler A., Dietrich D., van Leenders G., Uhl B., Hoogland M., Handle F., Schlick B., Neuwirt H., et al. PIAS1 is a determinant of poor survival and acts as a positive feedback regulator of AR signaling through enhanced AR stabilization in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2015;35:2322–2332. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.292. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

