Refinement of the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Synovitis Model in Equine Middle Carpal Joints
- PMID: 40941269
- PMCID: PMC12427284
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15172474
Refinement of the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Synovitis Model in Equine Middle Carpal Joints
Abstract
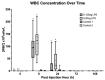
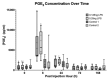
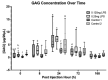
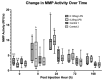
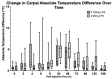
The aim of this study was to refine the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced synovitis model in normal carpal joints of Thoroughbred horses by comparing two low LPS doses. A further aim was to investigate the relationship between the induced synovitis and lameness. The study design consisted of two phases using nine horses with a unilateral crossover design and a within-animal saline control. Synoviocentesis was performed at post-injection hour (PIH) 0, 8, 24, 72 and 168, allowing for synovial fluid cytology and biomarker analysis. Objective gait and thermographic analysis were used to objectively measure clinical effects. The results demonstrate that injection of either a 0.125 ng or 0.25 ng dose of LPS induces a comparable degree of synovitis in terms of TP, WBC, PGE2 and MMP activity at peak values. Statistically significant changes in baseline lameness values were not detected with the 0.125 ng dose, a novel and valuable finding suggesting a comparable degree of synovitis is achieved without significant lameness. All measured parameters had returned to baseline by PIH 168. In conclusion, the findings of this study confirm that this LPS model produces a consistent and reliable synovitis at 0.25 ng and 0.125 ng doses. The reduction in lameness evident at the 0.125 ng dose offers enhanced animal welfare while delivering measurable synovitis. The authors believe that a further reduction in the LPS dose is possible with continued development of a repeated low-dose/slow-release model to better mimic clinical disease.
Keywords: equine; joint; lipopolysaccharide; model; synovitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Firth E.C., Wensing T., Seuren F. An Induced Synovitis Disease Model in Ponies. Cornell Vet. 1987;77:107–118. - PubMed
-
- Kay A.T., Bolt D.M., Ishihara A., Rajala-Schultz P.J., Bertone A.L. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects of Intra-Articular Injection of Triamcinolone Acetonide, Mepivacaine Hydrochloride, or Both on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lameness in Horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2008;69:1646–1654. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.69.12.1646. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ross T.N., Kisiday J.D., Hess T., McIlwraith C.W. Evaluation of the Inflammatory Response in Experimentally Induced Synovitis in the Horse: A Comparison of Recombinant Equine Interleukin 1 Beta and Lipopolysaccharide. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012;20:1583–1590. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2012.08.008. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

