Dynamics of Biochemical Parameters, Inflammatory and Stress Markers in Lambs Undergoing Caudectomy Using Two Different Methods
- PMID: 40941409
- PMCID: PMC12427419
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15172614
Dynamics of Biochemical Parameters, Inflammatory and Stress Markers in Lambs Undergoing Caudectomy Using Two Different Methods
Abstract
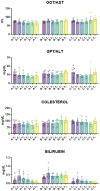
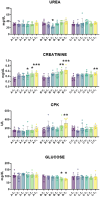
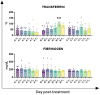
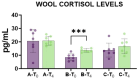
Zootechnical practices such as tail docking are still in use in dairy sheep farming, performed in the first week of life, mainly by rubber ring and only rarely by surgical methods. In this study, we evaluated the impact of caudectomy on ovine stress levels, inflammation, and health status by comparing tail docking carried out using rubber rings or surgical amputation. Twenty-one lambs were randomly selected and equally allocated into three groups: controls (n = 7), lambs with tail cut by rubber rings (n = 7), and lambs with caudectomy performed by surgical practice (n = 7). Several biochemical parameters and inflammatory markers were monitored at different times post-caudectomy, as well as wool levels of the stress marker cortisol. Our data revealed that lambs that underwent tail docking by rubber rings, but not by surgical procedure, presented inflammation and stress, as well as a moderate increase in muscular damage markers. These results are useful for the evaluation of animal welfare in dairy sheep that underwent caudectomy, highlighting the need to re-evaluate this procedure, as well as the ways in which it is performed.
Keywords: biochemical profile; caudectomy; cortisol; inflammatory status; sheep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Orihuela A., Ungerfeld R. Tail docking in sheep (Ovis aries), A review on the arguments for and against the procedure, advantages/disadvantages, methods, and new evidence to revisit the topic. Liv. Sci. 2019;230:103837. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2019.103837. - DOI
-
- Guatteo R., Guemene D. Sources of known and/or potential pain in farm animals. Adv. Anim. Biosci. 2014;5:319–332. doi: 10.1017/S204047001400020X. - DOI
-
- Trentini R., Maitino A.G., Di Fede E., Iannetti L., Dalla Villa P. Taglio della coda degli ovini e benessere animale, revisione della letteratura. Large Anim. Rev. 2013;19:21–31.
-
- Fisher M.W., Gregory N.G. Reconciling the differences between the length at which lambs’ tails are commonly docked and animal welfare recommendations. Proc. N. Z. Soc. Anim. Prod. 2007;67:32–38.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

