Biotechnological Advances in Sanguinarine and Chelerythrine Production from Plume Poppy (Macleaya cordata): A Gene Editing Perspective
- PMID: 40941831
- PMCID: PMC12430583
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14172667
Biotechnological Advances in Sanguinarine and Chelerythrine Production from Plume Poppy (Macleaya cordata): A Gene Editing Perspective
Abstract
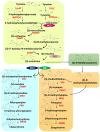
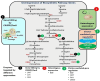
Plume poppy (Macleaya cordata), an important member of the Papaveraceae family, is a substantial source of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids (BIAs) such as sanguinarine and chelerythrine. These compounds possess significant therapeutic potential, including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antimicrobial activities, along with various industrial applications. However, the yield of these compounds in native plants are minimal and highly variable due to certain ecological factors. Recent advances in transgenic technologies have opened a new avenue for enhancing the biosynthesis of BIAs and optimizing their delivery in plume poppy. This review consolidates recent strategies in gene editing and metabolic modulations aimed at improving alkaloid biosynthesis in plume poppy. It uniquely connects these tools with industrial and therapeutic demands, offering a roadmap for enhanced BIA production. The current review also provides new insights into the overcoming the current limitations, offering potential solutions for stable, high-yield production of BIAs in plume poppy for their therapeutic use.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; chelerythrine; plume poppy; sanguinarine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yang Y., Sun Y., Wang Z., Yin M., Sun R., Xue L., Huang X., Wang C., Yan X., Li W., et al. Full-Length Transcriptome and Metabolite Analysis Reveal Reticuline Epimerase-Independent Pathways for Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids Biosynthesis in Sinomenium acutum. Front. Plant Sci. 2022;13:1086335. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1086335. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zuo Z., Zheng Y., Liang Z., Liu Y., Tang Q., Liu X., Zhao Z., Zeng J. Tissue-Specific Metabolite Profiling of Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids in the Root of Macleaya cordata by Combining Laser Microdissection with Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017;31:397–410. doi: 10.1002/rcm.7804. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

