SMART MAT: Fibre Optic Innovation for Bedside Monitoring and Validation of Continuous Vital Signs
- PMID: 40942752
- PMCID: PMC12431380
- DOI: 10.3390/s25175321
SMART MAT: Fibre Optic Innovation for Bedside Monitoring and Validation of Continuous Vital Signs
Abstract
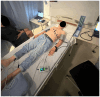
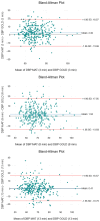
Vital sign monitoring is fundamental to patient care. Although traditional intermittent systems are flawed, barriers to implementing continuous monitoring systems remain. The SMART MAT is a novel continuous monitoring device that detects vital signs remotely via fibre optic technology. The study aims to validate the SMART MAT and its paired devices against gold/clinical standard measurements for measuring heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (RR), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), and oxygen saturation (SpO2). Healthy adults aged 21 to 80 were recruited for this cross-sectional study. Participants rested supine on a standardised mattress with the SMART MAT below. Vital signs were recorded over three five-minute intervals. Statistical analysis included descriptive statistics, two-way ANOVA, Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), and Bland-Altman plots. Among 321 participants recruited, HR and most RR measurements saw non-statistically significant differences (p > 0.05). Statistically significant differences were observed for SBP, SpO2, and most DBP measurements (p < 0.05). Only SBP measurements exceeded the acceptable limits of differences. Effect sizes were small to negligible (n2 < 0.04) and MAPE values were <20%. The SMART MAT has demonstrated reasonable accuracy and validity in monitoring vital signs in healthy adults. Alternative paired BP devices are recommended to enhance SBP measurement accuracy.
Keywords: continuous monitoring; fibre optic technology; healthcare technology; patient care; remote monitoring; vital sign monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures










References
-
- Doyle D.J. Clinical Early Warning Scores: New Clinical Tools in Evolution. [(accessed on 21 June 2025)];Open Anesth. J. 2018 12:26–33. doi: 10.2174/2589645801812010026. Available online: https://openanesthesiajournal.com/VOLUME/12/PAGE/26/FULLTEXT/ - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

