A Novel ML-Powered Nanomembrane Sensor for Smart Monitoring of Pollutants in Industrial Wastewater
- PMID: 40942817
- PMCID: PMC12431498
- DOI: 10.3390/s25175390
A Novel ML-Powered Nanomembrane Sensor for Smart Monitoring of Pollutants in Industrial Wastewater
Abstract
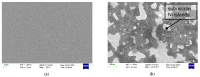
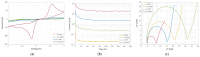
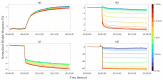
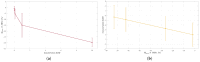
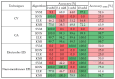
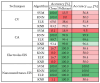
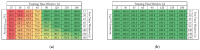
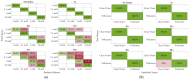
This study presents a comprehensive analysis aimed at validating the use of an innovative nanosensor based on graphitic nanomembranes for the smart monitoring of industrial wastewater. The validation of the potential of the nanosensor was carried out through the development of advanced analytical methodologies, a direct experimental comparison with commercially available electrode sensors commonly used for the detection of chemical species, and the evaluation of performance under conditions very similar to real-world field applications. The investigation involved a series of controlled experiments using an organic pollutant-benzoquinone-at varying concentrations. Initially, data analysis was performed using classical linear regression models, representing a conventional approach in chemical analysis. Subsequently, a more advanced methodology was implemented, incorporating machine-learning techniques to train a classifier capable of detecting the presence of pollutants in water samples. The study builds upon an experimental protocol previously developed by the authors for the nanomembranes, based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The results clearly demonstrate that integrating the nanosensor with machine-learning algorithms yields significant performance. The intrinsic properties of the nanosensor make it well-suited for potential integration into field-deployable platforms, offering a real-time, cost-effective, and high-performance solution for the detection and quantification of contaminants in wastewater. These features position the nanomembrane-based sensor as a promising alternative to overcome current technological limitations in this domain.
Keywords: data analysis; environmental monitoring; industrial wastewater; machine learning; nanosensor; pollutant detection; smart monitoring.
Figures



References
-
- Shrestha R., Ban S., Devkota S., Sharma S., Joshi R., Tiwari A.P., Kim H.Y., Joshi M.K. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021;9:105688. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105688. - DOI
-
- Qasem N.A., Mohammed R.H., Lawal D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. npj Clean Water. 2021;4:36. doi: 10.1038/s41545-021-00127-0. - DOI
-
- Adetunji A.I., Olaniran A.O. Treatment of industrial oily wastewater by advanced technologies: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2021;11:98. doi: 10.1007/s13201-021-01430-4. - DOI
-
- Ghasemi N., Zare F., Hosano H. A review of pulsed power systems for degrading water pollutants ranging from microorganisms to organic compounds. IEEE Access. 2019;7:150863–150891. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2947632. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

