Transgenerational Effects and Heritability of Folate Receptor Alpha Autoantibodies in Autism Spectrum Disorder
- PMID: 40943215
- PMCID: PMC12428755
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26178293
Transgenerational Effects and Heritability of Folate Receptor Alpha Autoantibodies in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
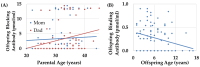
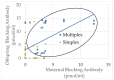
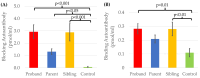
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) affects an estimated prevalence of 1 in 31 children but the cause in most cases is unknown. Human and animal studies have linked ASD to Folate Receptor Alpha Autoantibodies (FRAAs). Our previous studies demonstrated that FRAAs are more common, on average, in families with children with ASD. This study reanalyzed data from a previous study which included 82 children diagnosed with ASD, 53 unaffected siblings, 70 mothers, 65 fathers, and 52 typically developing controls who did not have a history of ASD in their family. This study investigates the association of FRAA titers with ASD risk factors and explores the relationship of FRAA titers across generations. Several known risk factors for ASD, including multiplex ASD families, multiple birth pregnancies, and increased maternal and paternal ages at birth, were related to offspring FRAA titers. Multiplex ASD families demonstrated higher FRAA titers. Significant correlation were found between maternal and offspring blocking FRAA titers. FRAA titers increased across generations, although the increase in blocking FRAA titers was only seen in multiplex families. The proband with ASD showed higher blocking but not higher binding, FRAA titers compared to their non-affected siblings. Paternal FRAA titers are associated with several measures of offspring behavior and cognitive development. This research highlights the potential transgenerational transmission of FRAAs and their role in ASD. This supports the notion that heritable non-genetic factors may be important in the etiology of ASD and that FRAAs may demonstrate anticipation (worsening across generations), especially in multiplex families. FRAAs may provide one example of the possibility that susceptibility to autoimmune processes may contribute to disrupted brain development and function in ASD.
Keywords: anticipation; autism spectrum disorder; cerebral folate deficiency; folate receptor alpha; folate receptor alpha autoantibodies; heritability.
Conflict of interest statement
E.V.Q. and J.M.S. are inventors on a US patent for the detection of FRAAs issued to the Research Foundation of the State University of New York, NY, USA. I.L.C. was involved in the development of the PDDBI and receives royalties from the use of this instrument. The remainder of the authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Association A.P. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®) 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; Washington, DC, USA: 2013.
-
- Shaw K.A., Williams S., Patrick M.E., Valencia-Prado M., Durkin M.S., Howerton E.M., Ladd-Acosta C.M., Pas E.T., Bakian A.V., Bartholomew P., et al. Prevalence and Early Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 4 and 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 16 Sites, United States, 2022. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2025;74:1–22. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7402a1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maenner M.J., Warren Z., Williams A.R., Amoakohene E., Bakian A.V., Bilder D.A., Durkin M.S., Fitzgerald R.T., Furnier S.M., Hughes M.M., et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2020. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2023;72:1–14. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7202a1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

