Medical Ozone Treatment Attenuates Male Reproductive Toxicity Induced by Bleomycin, Etoposide, and Cisplatin Regimen in an Experimental Animal Model
- PMID: 40943467
- PMCID: PMC12428823
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26178547
Medical Ozone Treatment Attenuates Male Reproductive Toxicity Induced by Bleomycin, Etoposide, and Cisplatin Regimen in an Experimental Animal Model
Abstract
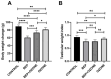
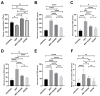
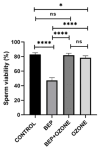
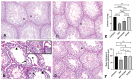
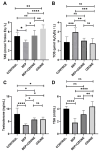
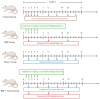
The chemotherapeutic combination of bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin (BEP) is well-documented to exert gonadotoxic effects, ultimately leading to impaired fertility. This experimental rat study investigated the potential protective role of repeated medical ozone therapy in mitigating the deleterious effects of BEP treatment in male rats. Thirty-two adult male Sprague Dawley rats were randomly assigned to four groups: (i) a healthy control group, (ii) a group receiving injections of the BEP regimen over nine weeks, (iii) a group receiving the same BEP regimen plus medical ozone (1 mg/kg IP) twice weekly, and (iv) a group receiving only ozone therapy. BEP treatment significantly reduced sperm concentration and increased morphological abnormalities, both of which were partially restored by ozone co-administration. Ozone therapy also elevated testosterone and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels when co-administered with BEP compared to BEP treatment alone. Oxidative stress analysis demonstrated that total oxidative status (TOS) and total antioxidant status (TAS) levels were significantly improved in the BEP + ozone group. Histopathological analysis revealed that ozone treatment ameliorated BEP-induced testicular damage, as evidenced by improved Johnsen scores and increased thickness of the seminiferous tubule epithelium. In conclusion, repeated medical ozone therapy appears to mitigate BEP-induced reproductive toxicity by preserving sperm quality, endocrine function, and redox homeostasis.
Keywords: bleomycin; cancer; chemotherapy; cisplatin; etoposide; infertility; medical ozone; oxidative stress; rat; sperm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ujah G.A., Nna V.U., Suleiman J.B., Eleazu C., Nwokocha C., Rebene J.A., Imowo M.U., Obi E.O., Amachree C., Udechukwu E.C., et al. Tert-butylhydroquinone attenuates doxorubicin-induced dysregulation of testicular cytoprotective and steroidogenic genes, and improves spermatogenesis in rats. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:5522. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85026-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moradi M., Hashemian M.A., Faramarzi A., Goodarzi N., Hashemian A.H., Cheraghi H., Jalili C. Therapeutic effect of sodium alginate on bleomycin, etoposide and cisplatin (BEP)-induced reproductive toxicity by inhibiting nitro-oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2024;14:1565. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52010-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aydoğdu İ., Ekin R.G., Yıldız P., Mirapoğlu S.L., Çay A., Aydoğdu Y.E., Kılınçaslan H., Semerci M.B., İlbey Y.Ö. Does Ozone Administration Have a Protective Effect Against Cisplatin induced Histological Changes in Rat Testis? J. Urol. Surg. 2019;6:32–37. doi: 10.4274/jus.galenos.2018.2225. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

