Nebulized Bacterioruberin/Astaxanthin-Loaded Nanovesicles: Antitumoral Activity and Beyond
- PMID: 40943526
- PMCID: PMC12429319
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26178607
Nebulized Bacterioruberin/Astaxanthin-Loaded Nanovesicles: Antitumoral Activity and Beyond
Abstract
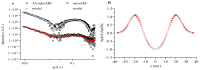
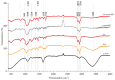
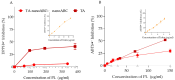
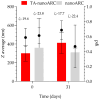
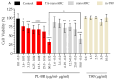
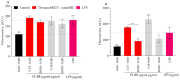
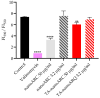
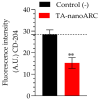
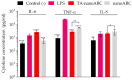
The membranes of halophilic archaea are a source of novel biomaterials, mainly of isoprenoid nature, with therapeutic properties practically unraveled. Here, we explored the antitumoral activity of neutral archaeolipids (NAs, such as bacterioruberin, astaxanthin, and dihydrosqualene) present in the total archaeolipids (TAs) (a fraction from the first step of lipid extraction by the modified Blight and Dyer technique) extracted from halophilic archaea Halorubrum tebenquichense, and formulated as TA-nanoarchaeosomes (TA: polar archaeolipids (PAs): Tween 80, 5:5:4 w:w:w, TA-nanoARC). The structure of 300.3 ± 84.2 nm TA-nanoARC of 0.59 ± 0.12 polydispersity index and -20 ± 3.7 mV ζ potential as determined by SAXS modelling, revealed that NA reduced the hydrophobic core and enlarged its hydrophilic section in comparison to TA-lacking bilayers (nanoARC), while preserving the width (~50 Å) and unilamellarity. Stable to storage and nebulization, TA-nanoARC was cytotoxic on A549 cells after 48 h, with an IC50 expressed as [bacterioruberin] of 0.15 μg/mL (~0.20 µM), comparable to or lower than the IC50 of docetaxel or cisplatin. Such cytotoxicity was exerted at a concentration harmless to macrophages (mTHP-1 cells). Besides, the conditioned medium from TA-nanoARC nebulized on A549 cells reduced the expression of the CD204/SRA-1, an M2 phenotype marker, and induced pro-inflammatory activity, comparable to or to a greater extent than that induced by lipopolysaccharide, including IL-6 and TNF-α, in mTHP-1 as a model of tumor-associated macrophages. The endocytosis of TA-nanoARC by A549 cells induced Lysotracker red fluorescence to fade and blur. This suggested the internalization of the highly viscous and ordered TA-nanoARC rich in NAs and subsequent lysosomal dysfunction (and not its antioxidant activity), as responsible for the selective damage on A549 cells. These are the first results showing that nebulized TA-nanoARC, lethal to A549 cells and modulating mTHP-1 cell phenotype, may act as antitumorals in the absence of cytotoxic drugs.
Keywords: inhalation; lungs; xanthophylls.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Treatment Options for Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)|Lung Cancer|Cancer Research UK. [(accessed on 27 June 2025)]. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/lung-cancer/treatment/non-....
-
- NSCLC Treatment|NSCLC Treatment Options|American Cancer Society. [(accessed on 27 June 2025)]. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/lung-cancer/treating-non-small-cell.....
-
- Postmus P.E., Kerr K.M., Oudkerk M., Senan S., Waller D.A., Vansteenkiste J., Escriu C., Peters S. Early and Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2017;28:iv1–iv21. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx222. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

