High-Resolution CT Findings in Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Connective Tissue Diseases: Differentiating Patterns for Clinical Practice-A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40943925
- PMCID: PMC12429569
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14176164
High-Resolution CT Findings in Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Connective Tissue Diseases: Differentiating Patterns for Clinical Practice-A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Abstract
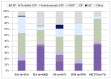
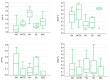
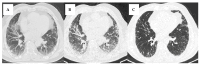
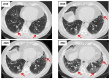
Objectives: Connective tissue diseases (CTDs) include a diverse group of systemic autoimmune conditions, among which interstitial lung disease (ILD) is acknowledged as a major determinant of prognosis. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is the gold standard for ILD assessment. The distribution of HRCT patterns across CTDs remain incompletely defined. The objective of this systematic review is to synthesize available evidence regarding the prevalence of specific radiological patterns within CTD-ILDs and to assess whether specific patterns occur at different frequencies among individual CTDs. Methods: The inclusion criteria encompassed original human studies published in English between 2015 and 2024, involving adult participants (≥18 years) with CTD-ILDs assessed primarily by HRCT and designed as retrospective, prospective, or cross-sectional trials with extractable data. We systematically searched PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science (January 2025). Risk of bias was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for cohort and case-control studies, and the JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for cross-sectional studies. Data were extracted and categorized by HRCT pattern for each CTD, and then summarized descriptively and statistically. Results: We analyzed 23 studies published between 2015 and 2024, which included 2020 patients with CTD-ILDs. The analysis revealed non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) as the most prevalent pattern overall (36.5%), followed by definite usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) (24.8%), organizing pneumonia (OP) (9.8%) and lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP) (1.25%). HRCT distribution varied by CTD: NSIP predominated in systemic sclerosis, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, and mixed connective tissue disease; UIP was most frequent in rheumatoid arthritis; LIP was more common in Sjögren's syndrome. While global differences were statistically significant, pairwise comparisons often lacked significance, likely due to sample size constraints. Discussion: Limitations include varying risk of bias across study designs, heterogeneity in HRCT reporting, small sample sizes, and inconsistent follow-up, which may reduce precision and generalizability. In addition to the quantitative synthesis, this review offers a detailed description of each radiologic pattern mentioned above, illustrated by representative examples to support the recognition in clinical settings. Furthermore, it includes a brief overview of the major CTDs associated with ILD, summarizing their epidemiological data, risk factors for ILD and clinical presentation and diagnostic recommendations. Conclusions: NSIP emerged as the most common HRCT pattern across CTD-ILDs, with UIP predominating in RA. Although inter-disease differences were observed, statistical significance was limited, likely reflecting sample size constraints. These findings emphasize the diagnostic and prognostic relevance of HRCT pattern recognition and highlight the need for larger, standardized studies.
Keywords: autoimmune lung involvement; connective tissue diseases; diffuse parenchymal lung disease; high-resolution computed tomography; imaging patterns; interstitial lung disease; radiologic features; rheumatologic lung disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


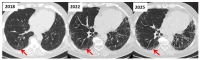

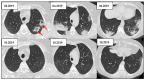
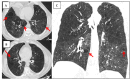

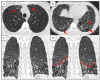


References
-
- Palmucci S., Galioto F., Fazio G., Ferlito A., Cancemi G., Di Mari A., Sambataro G., Sambataro D., Zanframundo G., Mauro L.A., et al. Clinical and radiological features of lung disorders related to connective-tissue diseases: A pictorial essay. Insights Imaging. 2022;13:108. doi: 10.1186/s13244-022-01243-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wuyts L.L., Camerlinck M., de Surgeloose D., Vermeiren L., Ceulemans D., Clukers J., Slabbynck H. Comparison between the ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT criteria of 2011 and 2018 for usual Interstitial Pneumonia on HRCT: A cross-sectional study. Br. J. Radiol. 2021;94:20201159. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20201159. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

